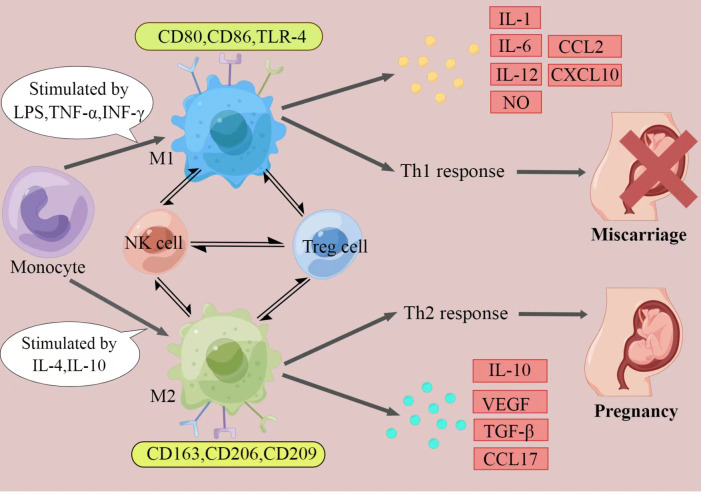
Figure 1.
The polarization of macrophages and their characteristics. The figure displays a general principle of polarized M1 and M2 macrophage. M1 and M2 phenotypes represent two extremes of macrophage polarization and display distinct functions, thereby result in different pregnancy outcomes. In response to different stimuli, decidual macrophages undergo M1-like, or M2-like activation. M1 macrophages are stimulated by LPS, TGF-α, or IFN-γ. They express CD80, CD86, and TLR-4, secrete IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, NO, CCL2 and CXCL10, and produce Th1 responses, exert pro-inflammatory effects. In contrast, M2 macrophages are activated by IL-4 or IL-10. They express CD163, CD206, and CD209, secrete IL-10, VEGF, TGF-β and CCL17, and promote Th2 responses, provide an immune-tolerant environment for the fetus. Thus, if M2 macrophages play the major role at the maternal-fetal interface, pregnancy would continue. When M1 macrophages are absolutely dominant, it will ultimately lead to miscarriage. (Created by Figdraw).