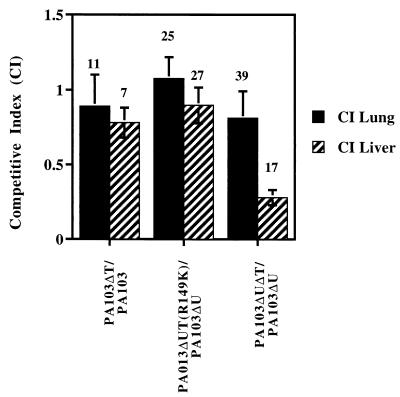
FIG. 7.
ExoT is required for full virulence in an animal model of acute pneumonia. Equal amounts of the indicated pairs of strains of bacteria were inoculated into the nares of mice. The lungs and livers of the mice were harvested 24 h later and homogenized, and serial dilutions were plated on selective medium to obtain counts of each bacterial strain. A competitive index was calculated by obtaining the ratio of the ExoT mutant strain counts to wild-type (with respect to ExoT expression) bacterial counts recovered from the lung or liver and comparing it to the same ratio obtained with the infecting inoculum (roughly 1.0 but calculated precisely for each experiment). A competitive index greater than 1.0 indicates that the ExoT mutant strain colonized better than the wild type, and a competitive index less than 1.0 indicates that the ExoT mutant strain was less efficient than the wild type in colonization. The number of animals used for each experiment is shown. Compared to PA103ΔU, PA103ΔUΔT was significantly impaired in its ability to colonize the liver (P = 0.06, Student's two-tailed t test).