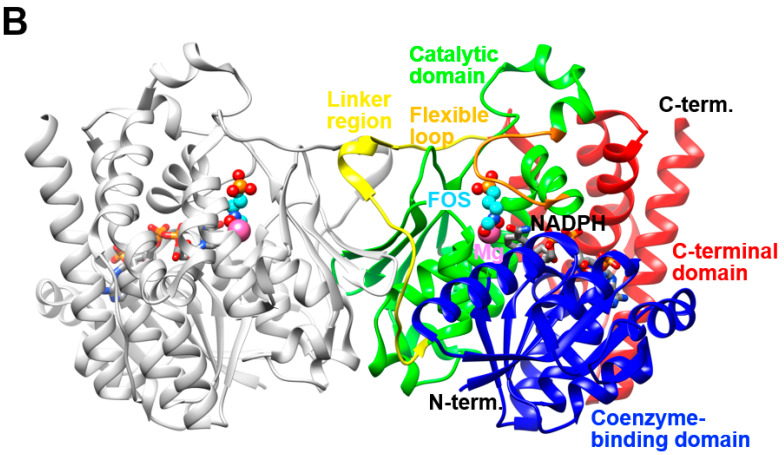
Figure 6.
(A): Amino acid sequence alignment of bacterial and parasitic DXRs. Residues involved in phosphate/phosphonate-, linker-, and metal and hydroxamate-binding are highlighted in blue, green, and red, respectively. The colored ribbons above the sequence alignment represent the respective domains in PfDXR: the NADPH-binding (blue), catalytic (green), and C-terminal (red) domains. The linker region and flexible loop in the catalytic domain are colored yellow and orange, respectively. The pink bars and cyan arrows represent the secondary structure elements, namely, α-helices and β-strands, respectively; (B): The overall structure of the quaternary (enzyme-NADPH-metal-inhibitor) complex of PfDXR (PDB 3AU9) [91]. Three domains, a linker region, and a flexible loop in the catalytic domain of one subunit are colored as in (A). The other subunit is colored grey. The bound fosmidomycin (FOS) and NADPH molecules are shown as ball-and-stick (cyan) and stick (grey) models, respectively. The bound magnesium ions are shown as sphere models (pink).