Figure 4.
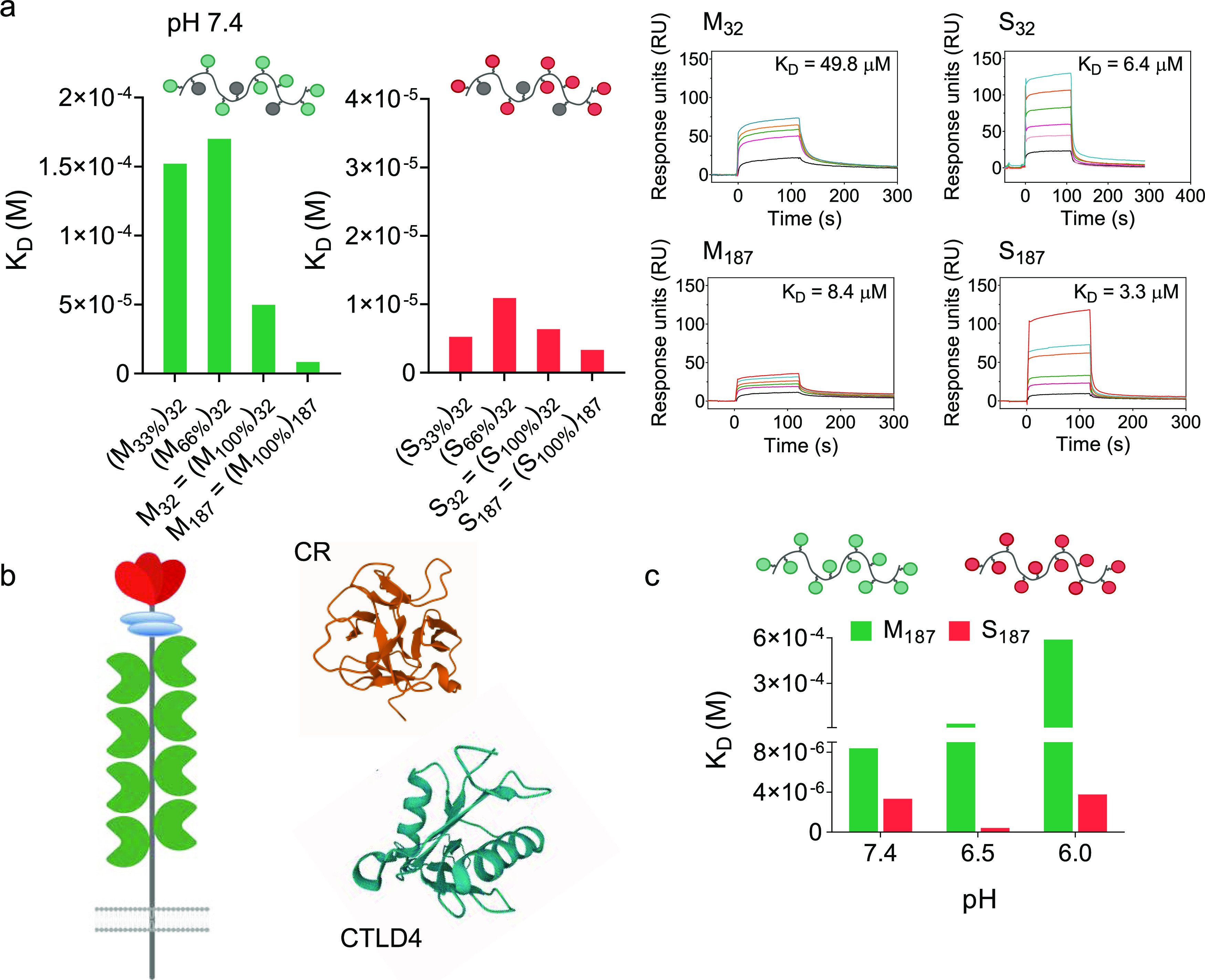
Differential pH dependency of mannosylated and sulfated glycopolymers binding to CD206. (a) Binding of Man and SO4-3-Gal glycopolymers to CD206 at pH 7.4, as assessed by SPR. Nature of sugar repeating units, their density along each polymer chain, and size of the glycopolymers are systematically varied, to identify a structure–activity relationship for these multivalent ligands. Representative SPR sensorgrams of binding profiles are shown for M32 and S32 and M187 and S187 at concentrations of polymer sugar repeating units of 0.032–2.4 mM. Sensorgrams of all polymers are shown in Figures S13 and S14. (b) Schematic representation of CD206, and crystal structures of its CR domain59 and CTLD4,58 PDB ID 1DQO and 1EGG from RCSB PDB, respectively. Images were produced with Mol*.60 (c) pH strongly affects binding of mannosylated M187 to CD206 but to a much lesser extent that of S187. Binding to CD206 is tested in the 7.4–6.0 pH range, to simulate the conditions which glycopolymer–CD206 complexes encounter when going from the cell membrane to endosomal compartments. Dissociation constant KD values are derived from SPR analysis, using immobilized CD206, in 10 mM HEPES, 5 mM CaCl2, 0.005% tween-20, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 6.5, 6. Higher KD values indicate more favorable dissociation of glycopolymer–CD206 complexes.
