Figure 6.
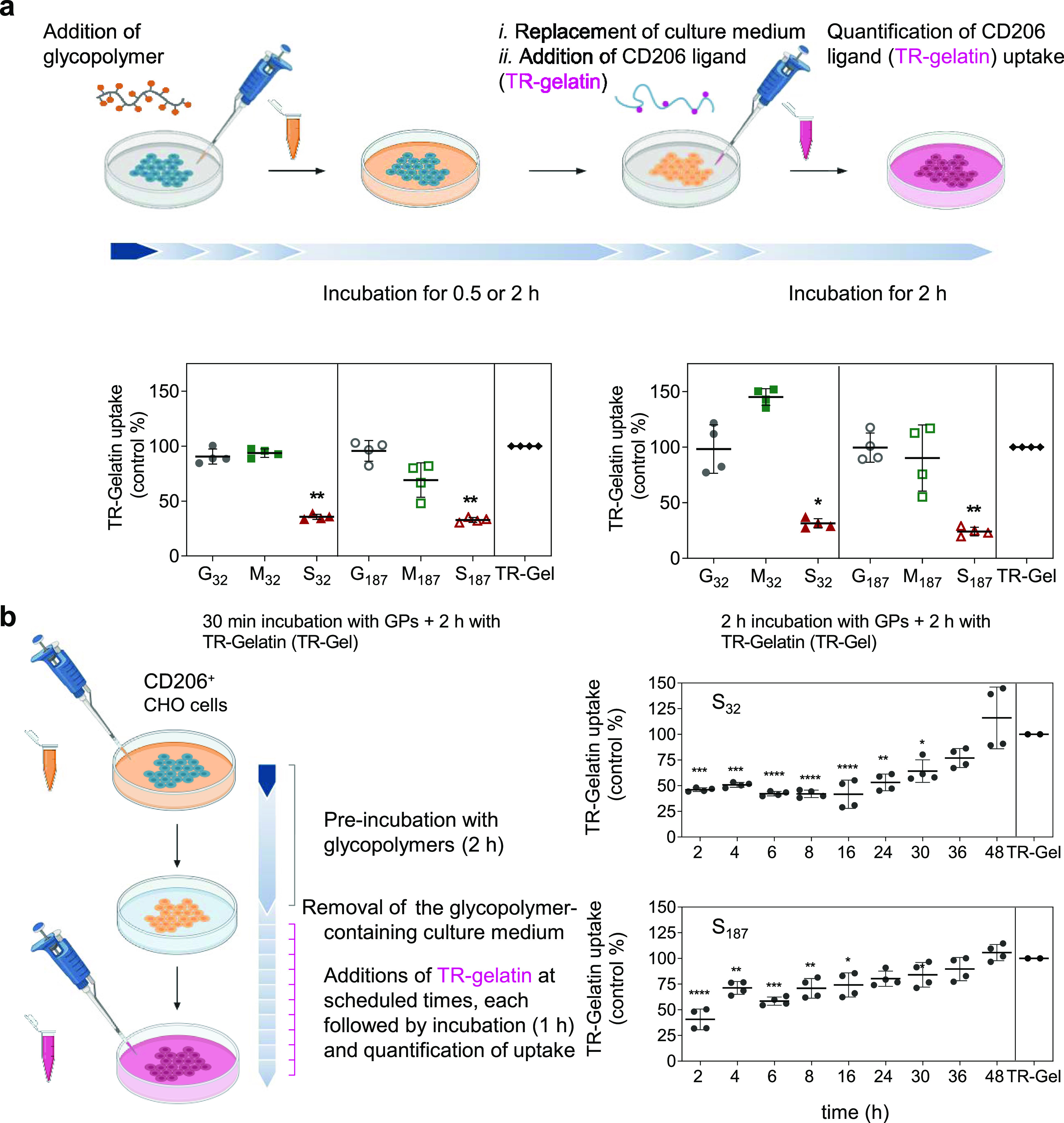
SO4-3-Gal glycopolymers inhibit CD206 endocytic activity in vitro. (a) SO4-3-Gal glycopolymers inhibit uptake of gelatin in CD206+-CHO cells. Cells were pre-treated with glycopolymers (GPs, 490 μM in sugar repeating units, 30 min, left panel, or 2 h, right panel), and then, the cells were washed and incubated with glycopolymer-free media containing Texas Red-tagged gelatin (TR-Gel, 10 μg mL–1), for 2 h. TR-gelatin uptake was quantified by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as a percentage of gelatin uptake compared to that of non-pre-treated cells (TR-Gel columns). Data are presented as mean ± s.d. of four biological replicates from two independent experiments. (b) Created with BioRender. Inhibition of CD206 endocytic activity by a single treatment with SO4-3-Gal glycopolymers is long-lasting yet reversible. CD206+-CHO cells were incubated for 2 h with S32 or S187 (490 μM in sugar repeating units). Control cells were incubated over the same period with a glycopolymer-free medium. After washing, cells were incubated with a fresh medium and at scheduled times treated with a pulse of TR-gelatin (80 μg mL–1) for 1 h. Gelatin uptake was quantified by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as a percentage of gelatin uptake compared to that of non-pretreated cells. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. of four biological replicates from two independent experiments. A one-way ANOVA was performed to test significance; *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, **P ≤ 0.001, and **** P ≤ 0.0001. Created with BioRender.
