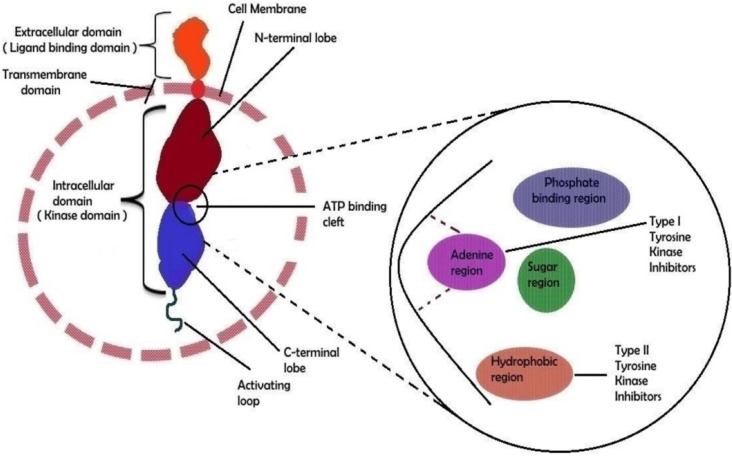
Figure 1.
The molecular structural feature of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). An RTK’s extracellular domain can bind particular ligands such as growth factors, whereas the intracellular domain is responsible for the kinase’s (auto)phosphorylation. The external and internal domains are separated by the transmembrane region, which is fixed in the cell membrane. The ATP-binding cleft is located between the two lobes of the intracellular domain. A schematic depiction of the ATP binding cleft with its numerous regions is shown on the right side of the image. Type I and type II tyrosine kinase inhibitor binding sites have been shown in a biochemical general structure model. Adapted from [30], Copyright 2021 MDPI.