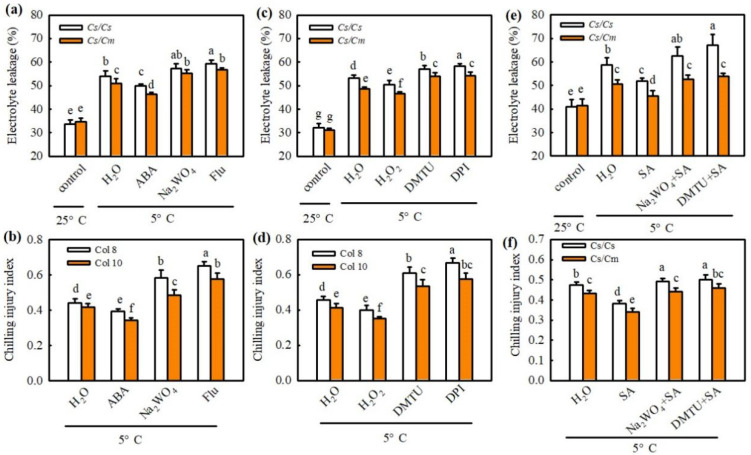
Figure 5.
The role of ABA and H2O2 in SA- or grafting-induced chilling tolerance in cucumber. (a) Electrolyte leakage of plants after chilling treatment for 0 h and 48 h. (b) Chilling injury index of plants after chilling treatment for 0 h and 72 h. Plants were foliar sprayed with 50 μM ABA, 3 mM Na2WO4, 50 μM fluridone, or distilled water (control) for 12 h and then exposed to chilling stress. (c) Electrolyte leakage of plants after chilling treatment for 0 h and 48 h. (d) Chilling injury index of plants after chilling treatment for 0 h and 72 h. Plants were foliar sprayed with 1 mM H2O2, 5 mM DMTU, 0.1 mM DPI, or distilled water (control) for 12 h and then exposed to chilling stress. (e) Electrolyte leakage of plants after chilling treatment for 0 h and 48 h or 72 h, respectively. (f) Chilling injury index of plants after chilling treatment for 0 h and 72 h. Plants were pretreated with 1 mM SA, 3 mM Na2WO4 + 1 mM SA, 5 mM DMTU + 1 mM SA, or distilled water (control) for 12 h and then exposed to chilling stress. Data are presented as the means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters indicate a statistical significance between samples at p < 0.05.