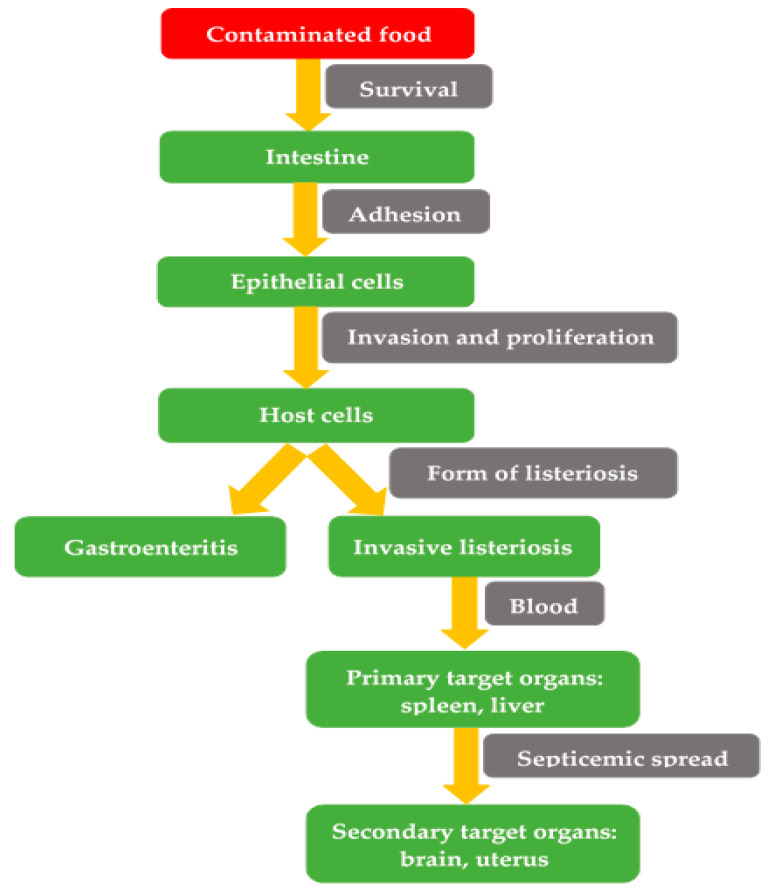
Figure 2.
Schematic L. monocytogenes infectious cycle in the human host. Bacteria enter the host through contaminated food and invade the epithelial cells, potentially causing gastroenteritis. Crossing the intestinal barrier, the bacteria spread via blood to their primary target organs (liver and spleen). Then, the bacteria may spread to secondary target organs (uterus, brain), resulting in abortion in pregnant women or meningoencephalitis, respectively.