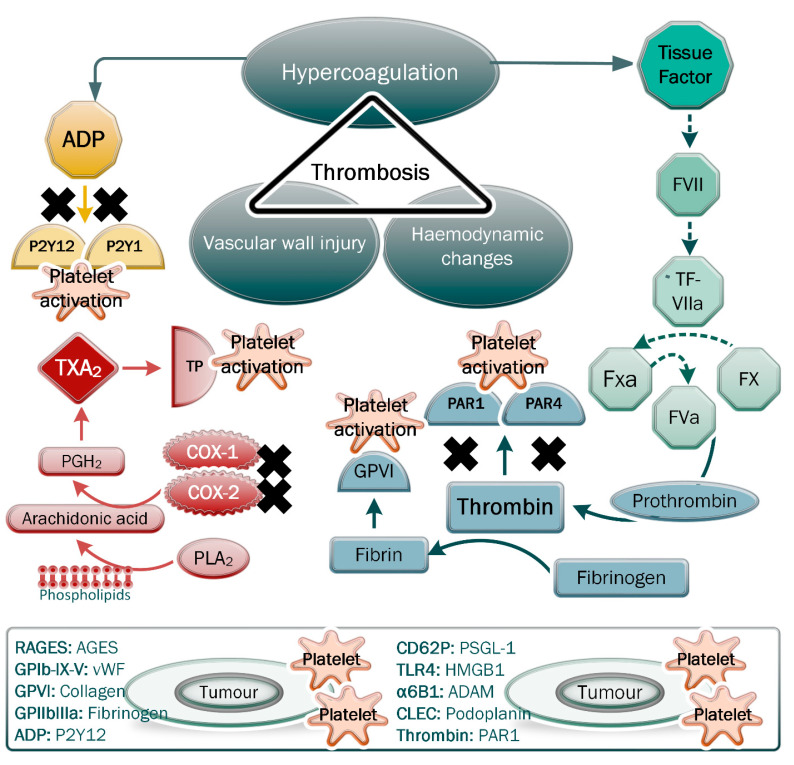
Figure 1.
Virchow’s triad showing the main parameters of thrombosis. Regarding hypercoagulation, note the effects of the secreted platelet agonist tissue factor, ADP, thrombin and thromboxane A2 on the pathways inducing platelet activation and fibrin formation. Tumour cells are able to secrete these platelet agonists, which, following induction of platelet activation, cause the release of microparticles and a host of factors that can facilitate tumour progression and thrombotic complications. The direct and indirect interactions between platelet receptors/ligands and cognate ligands/receptors on tumour cells are shown. The inhibition of PAR1 and PAR4 receptors, the P2Y12 and P2Y1 receptors, and the production of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) are indicated as mechanisms that prevent platelet activation and downstream effects.