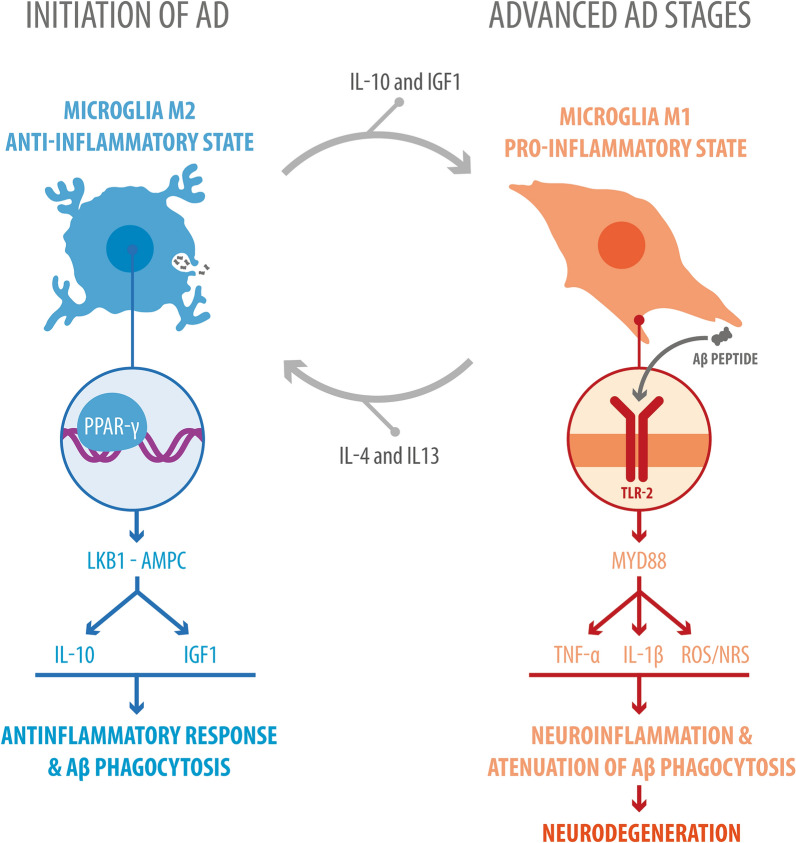
Fig. 2.
Vicious cycle of neuroinflammation with Aβ and tau. Aβ and tau activate microglia and astrocytes to produce ROS, RNS, and proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and TNF-α, inducing neuroinflammation. In turn, neuroinflammation increases the levels of Aβ and tau (because it is involved in the hyperphosphorylation of tau and attenuates the clearance of Aβ) or causes neurodegeneration in different ways (for example, via the PAP-2, GMF, ROS and RNS pathways). Neurodegeneration exacerbates neuroinflammation because the remains of dead cells and the tau that remains in the extracellular environment due to cell death activate microglia and astrocytes. This increased neuroinflammation also increases the Aβ and tau levels (for the same reasons as in the initial neuroinflammation)