Table 1.
Natural materials used to prepare 3D scaffolds.
| Natural Materials and Their Chemical Structure | SPR | Merits | Demerits | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Collagen 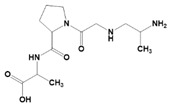
|
Hydrogen bonds hold the structure. Presence of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. |
Biocompatible and biodegradable. Non-toxic. Less immunogenic. Extracellular matrix secretion. |
Poor mechanical properties. Less stable. |
[44] |
Fibrinogen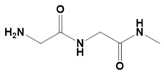
|
Presence primary and secondary amines in the structure. It consists of polypeptide chains. |
High cellular uptake. Hemostatic properties. High cell adhesion properties. High surface-to-volume ratio. |
Fast degradation. Poorly stable. |
[41] |
Gelatin [45,46]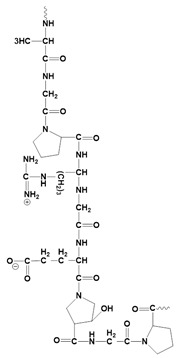
|
Consists of glycine, proline, and 4-hydroxyproline. | It can be used as a crosslinking agent. It helps to enhance the expansion ratios of other polymers. Excellent cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation properties. Less immunogenic. Biodegradable. Biocompatible. |
Low stability. | [45,46] |
| Keratin | Presence of cysteine residues. Structural stability comes from intermediate filaments. |
Excellent cell proliferation properties. Self-assemble. High cell viability. Controlled release properties. Time-dependent degradation profile. |
Poor structural integrity at biological environment. | [47] |
Starch 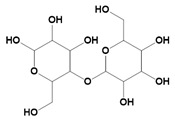
|
Consists of α-glycans. Carbohydrates. |
Cytocompatibility. Excellent cell adhesion profiles. Highly hydrophilic Biodegradable. Suitable for photothermal therapy. |
High water absorption ability. Poor mechanical properties. Difficult to chemical modification. |
[48] |
Chitosan 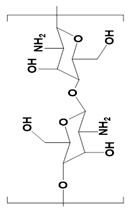
|
Linear polysaccharides. Beta-(1→4)-linked D-glucosamine |
Highly porous structure. Hemostatic properties. High thermal stability. Inhibits liver metastasis. Inhibits growth factor-based proliferation of tumor cells. |
Poor solubility in water. Susceptible to proteolytic enzymes. |
[49,50] |
Chitin 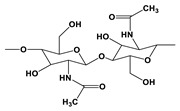
|
Presence of N-acetylglucosamine and N-glucosamine | It can be used for tissue repairing after breast cancer surgery. Non-toxic. Anti-inflammatory. Inhibits angiogenesis in tumors. |
Poor stability. Poor solubility. |
[51] |
Agarose 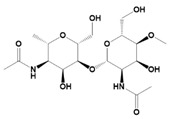
|
Agarobiose units are linked by hydrogen bonds. | Injectable in liquid form that later forms gel at body temperature. Excellent for cell delivery to target organs. It does not enhance immunogenicity. Biocompatible and biodegradable. |
Non-degradable. Poor cell attachment. |
[52,53] |
Alginate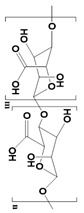
|
Different units of alginate have different properties. Presence of -COOH groups that can be chemically linked with anticancer drugs. Presence of guluronate units that inhibit metastasis. |
It can mimic natural ECM. Inhibits tumor cell proliferations due to gel-forming properties at body temperature. Highly hydrophilic. Biocompatible and biodegradable. |
Poor mechanical strength. Difficult to use in cell-based anticancer therapy due to poor cell adhesion properties. |
[54] |
Cellulose 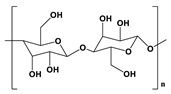
|
The glucose units are linked by glycosidic bonds and thereby form a polysaccharide structure. | Excellent mechanical properties. Hydrophilic in nature. Non-toxic. |
Non-degradable. | [55] |
Hyaluronic acid (HA) 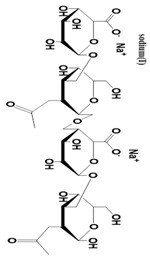
|
It consists of repeating disaccharide units. Presence of -OH and -COOH groups on the surface that can be chemically crosslinked with anticancer drugs. |
High drug-loading properties. Facilitates tumor cell targeting properties. High degradable profile. Non-immunogenic. |
Poor degradation profile. Unstable structure due to poor mechanical properties. |
[56] |
Glycosaminoglycans 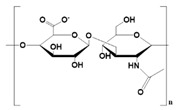
|
Individual disaccharide units are linked together by glycosidic bonds. | Anticancer activity. Prevents blood clots. Inhibits inflammatory pathway. Inhibition of metastasis. |
Microbial Contamination. | [57] |
