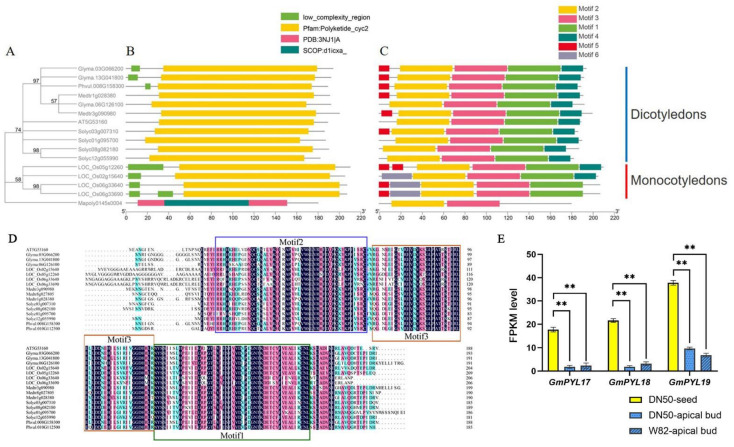
Figure 1.
PYL8 genes in Glycine max, Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Medicago truncatula, Solanum lycopersicum, and Marchantia polymorpha. (A) Phylogenetic trees of six species constructed by the Maximum Likelihood were adopted using MEGA 10.0 software, with 1000 bootstrap replicates. (B) Analysis of the conserved domains PYLs. (C) The gene-conserved motifs of PYLs genes in six species are based on phylogenetic relationships. Monocotyledons and dicotyledons are represented by red and blue, respectively. (D) Amino acid sequence of motif1 (green box), motif2 (blue box), and motif3 (red box) of PYLs in six species. (E) FPKM of GmPYL17, GmPYL18, and GmPYL19 in different tissues were determined from the transcriptome. The tissues are dry seed, shoot apical meristem of DN50, and Williams 82 (W82) plants. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). Student’s t-tests indicate significant differences in mean values relative to the mean value of seeds (** p < 0.01).