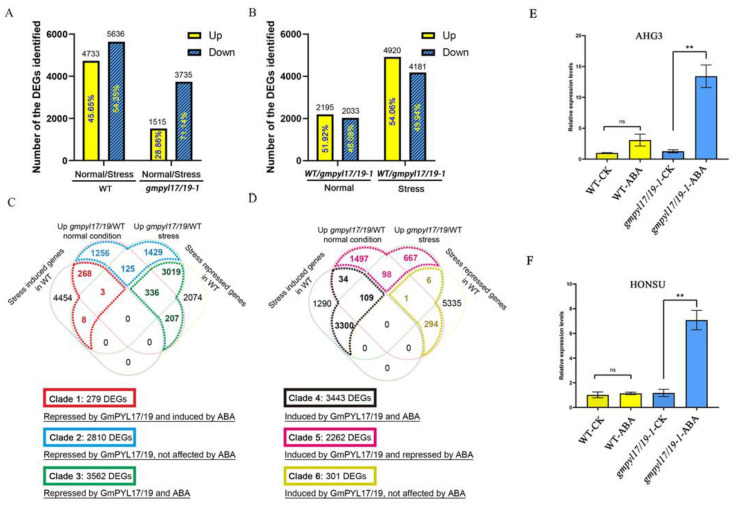
Figure 6.
Overview of the RNAseq analysis and the six clades of DEGs regulated by GmPYL17/19. (A,B) Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in comparing different lines and treatments. Normal in the plot indicates water, no ABA treatment, and stress indicates using 10 μM ABA stress treatment. p-value (adjusted p-value) < 0.05 and absolute log2 ratio > 1 were used for significant differential expression cutoffs. (C,D) Venn diagram of the DEGs in different genotypes under normal and ABA stress. Based on their expression patterns, the DEGs affected by the interaction of GmPYL17/19 and ABA stress and the GmPYL17/19 alone can be grouped into six different clades. The upregulated DEGs in the gmpyl17/19-1 mutant panel (C) were grouped into Clades 1–3 (279 DEGs, 2810 DEGs, and 3562 DEGs) based on how they responded to ABA stress (C). The upregulated DEGs in the gmpyl17/19 mutant panel (D) were grouped into Clades 4–6 (3443 DEGs, 2262 DEGs, and 301 DEGs) based on how they responded to ABA stress (D). The colors in the same clade were boxed the same color as in the Venn diagram. (E) Transcriptional levels of AHG3 in WT and the mutant of soybean gmpyl17/19-1 under greenhouse conditions (14 h light/10 h dark). (F) Transcriptional levels of HONSU in WT and the mutant of soybean gmpyl17/19-1 under greenhouse conditions. The values shown are relative to the control gene TUB and represent the means ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.) of three biological replications. Significant differences were identified by Student’s t-test (** p < 0.01; ns p > 0.05).