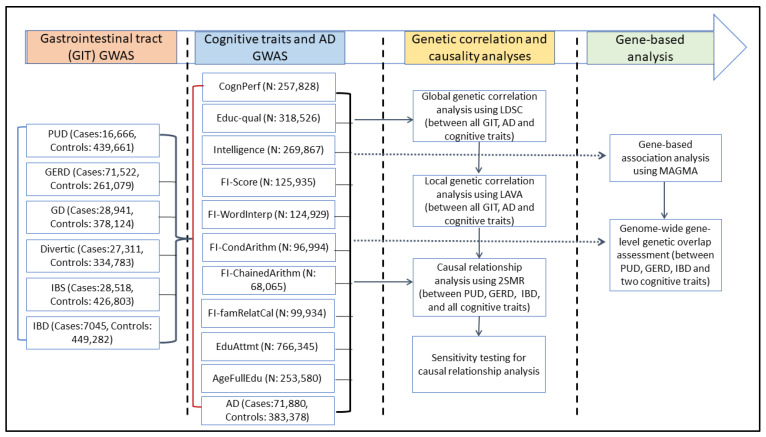
Figure 1.
Study design and workflow: examining the relationship of cognitive traits and AD with GIT disorders. AD: Alzheimer’s disease, IBS: irritable bowel syndrome, PUD: peptic ulcer disease, GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease, IBD: inflammatory bowel disease, GD: gastritis-duodenitis, Divertic: diverticulosis, AgeFullEdu: age completed full-time education, FI-ChainedArithm: fluid intelligence-chained arithmetic, FI-CondArithm: fluid intelligence-conditional arithmetic, FI-famRelatCal: fluid intelligence-family relationship calculation, FI-WordInterp: fluid intelligence-word interpolation, CognPerf: cognitive performance, Educ-qual: educational qualification, EduAttmt: educational attainment. GWAS: genome-wide association studies, GIT: gastrointestinal tract, LDSC: linkage disequilibrium score regression, LAVA: local analysis of [co]variant association, MAGMA: multi-marker analysis of genomic annotation, 2SMR: two-sample Mendelian randomisation.