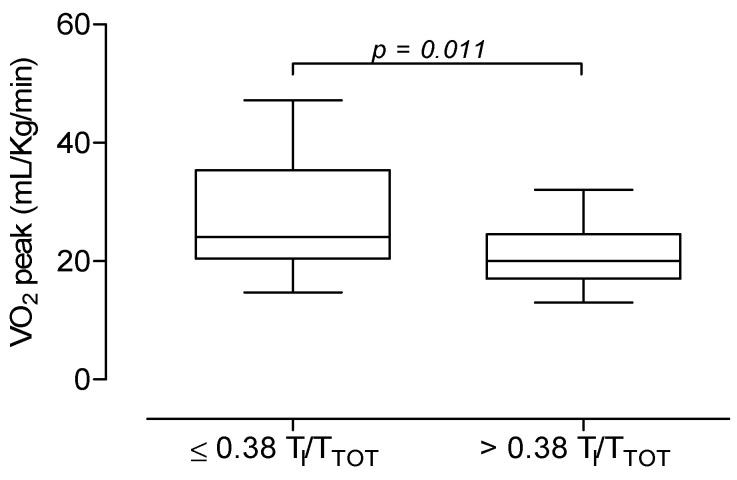
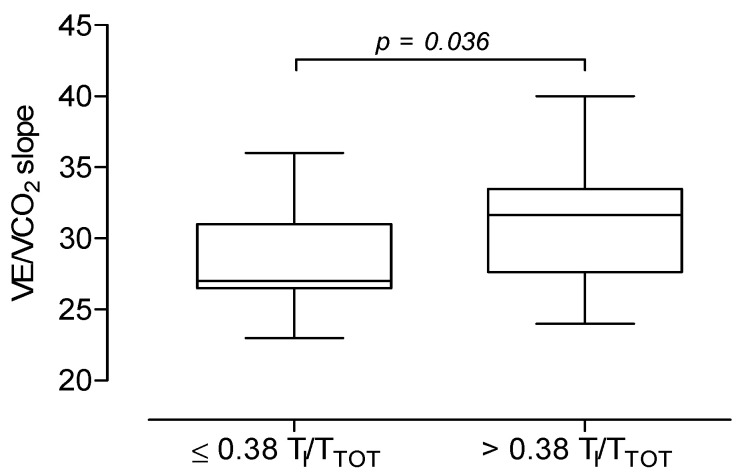
Figure 4.
Mean, SD and range values of VO2 peak (upper panel) and of VE/VCO2 slope (lower panel) in 13 Long-COVID patients with TI/TTOT ≤ 0.38 and in 29 Long-COVID patients with TI/TTOT > 0.38 at peak of exercise. Sing et al. [19] also demonstrated a hyperventilatory response during exercise in all patients. Similarly, in a large cohort of patients at approximately three months after the initial diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Motiejunaite et al. [5] found an elevated VE/VCO2 slope in one third of the study participants, suggesting a high incidence of inadequate ventilation on exertion. In the current study, LC patients had higher values in VE/VCO2 slope, as compared to controls, but they did not differ in terms of PETCO2, thereby showing ventilatory inefficiency without hyperventilation.