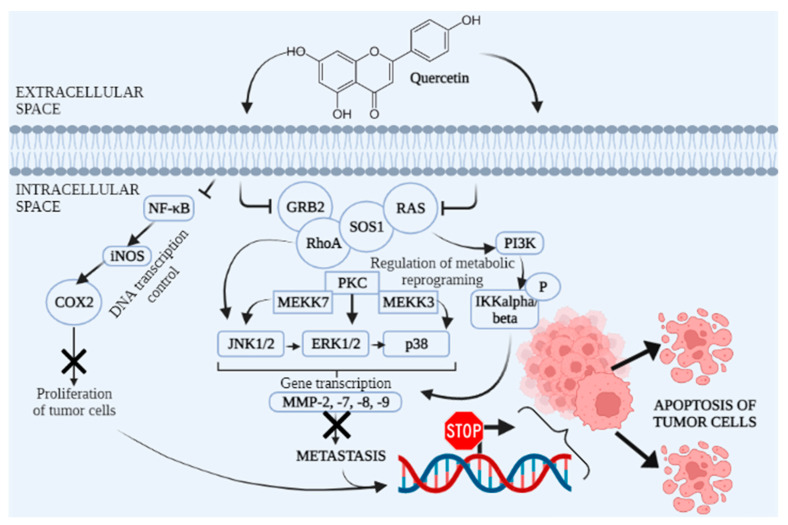
Figure 3.
Scheme of quercetin antitumor mechanisms of action. NF-κB (Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells)-iNOS (Inducible nitric oxide synthase)-COX2 (Cyclooxygenase 2) is an inflammatory signalling pathway which is blocked by quercetin induction in the tumour cell. It results in blockade of proliferation of tumour cells. Moreover, quercetin inhibits interaction of GRB (Growth factor receptor-bound protein), RhoA (Ras homolog family member A), SOS1 (Son of Sevenless 1) and RAS (Rat sarcoma virus), which prevents further metabolic reprograming. That includes inhibition of other metabolic molecules; PKC (Protein kinase C), MEKK-3, -7 (Mitogen-activated protein/ERK kinase -3, -7), JNK1/2 (c-Jun N-Terminal Protein Kinase 1/2), ERK1/2 (Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2), p38 (Mitogen-activated protein kinase), PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase), IKKalpha/beta (Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta) and, ultimately, further genetic transcription through MMP-2, -7, -8, and -9 (Matrix metalloproteinases). Finally, these events lead to tumour cell apoptosis.