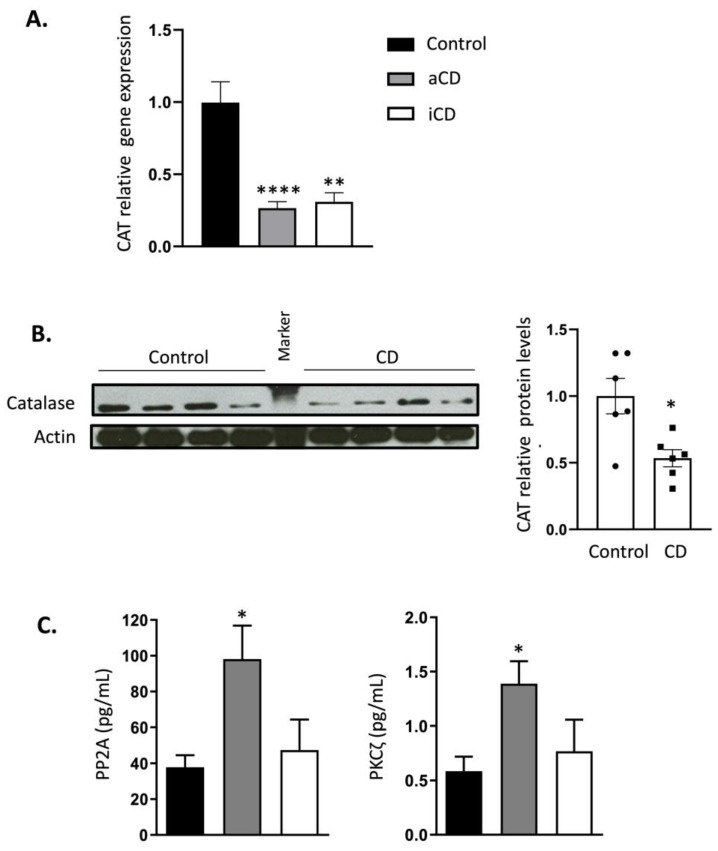
Figure 1.
Permanent CAT inhibition in leukocytes isolated from Crohn’s disease (CD) patients. (A). Gene expression analysis of CAT in the controls and active and inactive CD patients (N = 18, 20, and 10, respectively). (B). A Western blot densitometer, normalized with α-actin; its quantification represented in a histogram. The protein levels of CAT in the controls were significantly higher than in CD patients (N = 6 and 6, respectively) normalized with α-actin. (C). The protein levels (pg/mL) of CAT regulators Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and Protein Kinase C zeta (PKCζ) in the controls; active and inactive CD patients (N = 7, 10, and 4, respectively). The levels of both regulators had increased more in CD than in the control and iCD patients. The results are shown as mean ± SEM. The differences between the controls and both the active and inactive CD patients (aCD and iCD, respectively) were assessed by Student’s t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.