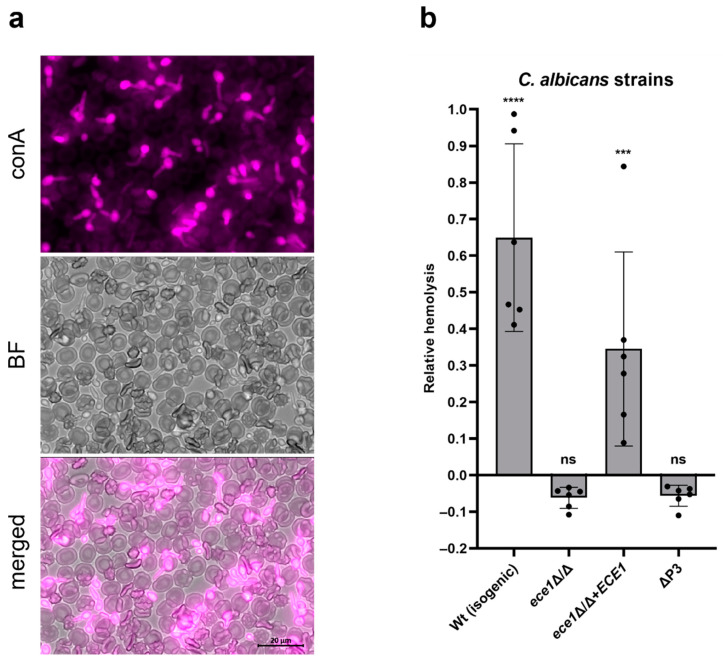
Figure 1.
Candida albicans lyses red blood cells (RBCs) by means of candidalysin. (a) C. albicans isogenic wild-type filamenting after 4 h incubation with RBCs. Fungal cells were stained with concanavalin A (conA, magenta). BF, bright field. (b) Purified RBCs were incubated with candidalysin-competent or -incompetent C. albicans strains for 24 h at 37 °C. Hemolysis was quantified by measuring the absorbance of sample’s supernatant at 414 nm, and plotted relative to the full lysis control sample (RBCs incubated with pure water), following subtraction of the vehicle control. Each data point in (b) represents a different donor (average of 2 technical replicates). Error bars show the standard deviation. For statistical analysis, an arbitrary value of 0.01 was assigned to any value that was below this threshold. Student’s paired t-tests, vs. the vehicle control, were then performed on log-transformed data. ***, p < 0.005; ****, p < 0.001; ns, not significant.