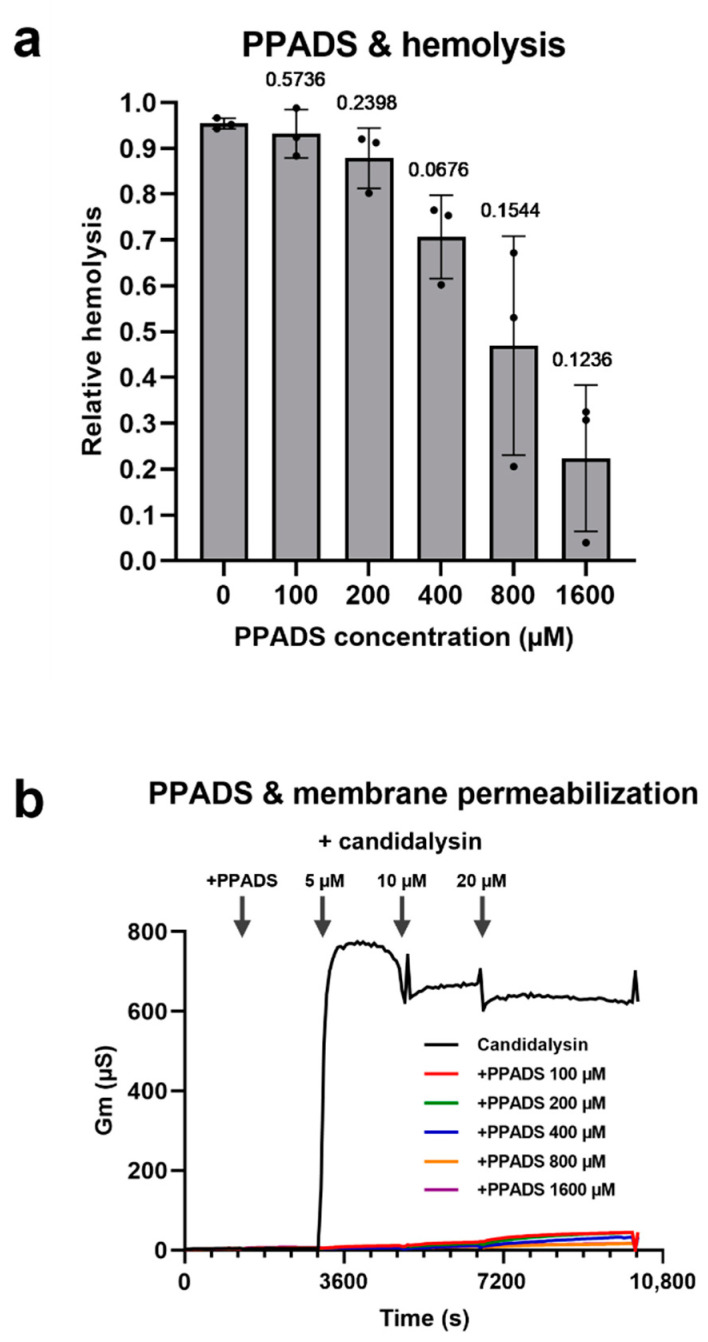
Figure 5.
The purinergic receptor antagonist pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2′,4′-disulfonic acid (PPADS) protects from candidalysin-induced hemolysis via a purinergic receptor-independent mechanism. (a) Purified RBCs were incubated with candidalysin (16 µM) and increasing concentrations of PPADS, for 1 h at 37 °C. Hemolysis was quantified by measuring the absorbance of sample’s supernatant at 414 nm, and plotted relative to the full lysis control sample (RBCs incubated with pure water and the same amount of PPADS), following subtraction of the relative vehicle control (containing the same amount of PPADS). Each data point on the graph represents a different donor (average of 2 technical replicates). Error bars show the standard deviation. For statistical analysis, student’s paired t-tests, vs. the candidalysin only sample, were then performed on log-transformed data. p values are depicted on top of each bar. (b) Synthetic membranes were incubated with the same increasing concentrations of PPADS as in (a) followed by addition of increasing concentrations of candidalysin, at 37 °C. Permeabilization was measured as kinetic changes in conductance of tethered lipid membranes.