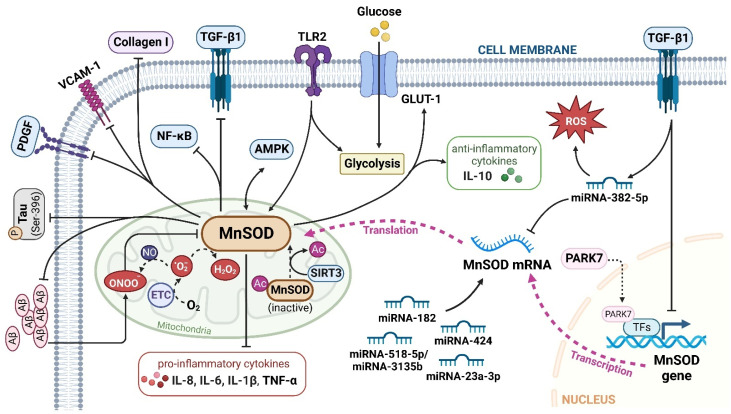
Figure 2.
The major signalling pathways involved in MnSOD regulation. MnSOD is localized in the mitochondrial matrix to catalyse the dismutation of O2•− to H2O2, and regulate cellular redox homeostasis. Multiple factors, cytokines, proteins, and miRNAs have been involved in the transcriptional and translational modulation of MnSOD. TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; TLR2, toll-like receptor 2; Aβ, amyloid, β-protein; GLUT-1, glucose transporter member 1; IL, interleukin; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; AMPK, adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase; P, phospho; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; ETC, electron transport chain; PARK7, Parkinson disease protein 7; TFs, transcriptional factors; Ac, acetyl; SIRT3, sirtuin 3. ‘↑’ represents increased or upregulated, while ‘⊥’ represents suppressed or downregulated (created with BioRender.com (accessed on 4 November 2022)).