Figure 2.
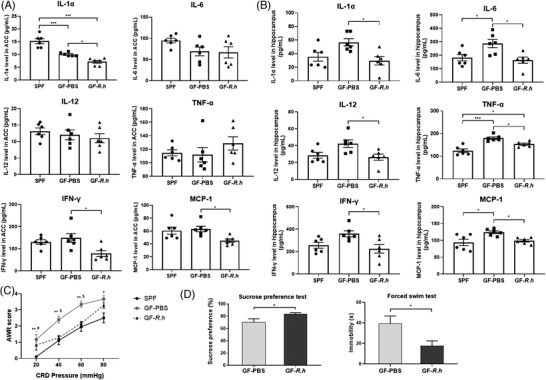
Effects of R. hominis on the levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the rat brain. Male SPF rats were orally treated with PBS for 5 days. Male GF rats were treated with R. hominis bacterial suspension (2 × 109 CFU day−1, GF‐R.h) or PBS (GF‐PBS) for 5 days. Behavioral experiments were performed 12 days after gavage. Cytokine (IL‐1α, IL‐6, IL‐12, TNF‐α, INF‐γ) and chemokine (MCP‐1) levels were determined 14 days after gavage. A) Levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) (n = 6). B) Levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the hippocampus (n = 6). *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001. One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post‐hoc test. C) Comparison of AWR scores among SPF, GF‐PBS, and GF‐R.h rats (n = 6–13). *, SPF versus GF‐PBS, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; #, SPF versus GF‐R.h, # p < 0.05; $, GF‐PBS versus GF‐R.h, $ p < 0.05. One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post‐hoc test. AWR, abdominal withdrawal reflex. D) The sucrose preference rate and immobility time between GF‐PBS and GF‐R.h rats (n = 6). *p < 0.05. Unpaired Student's t test.
