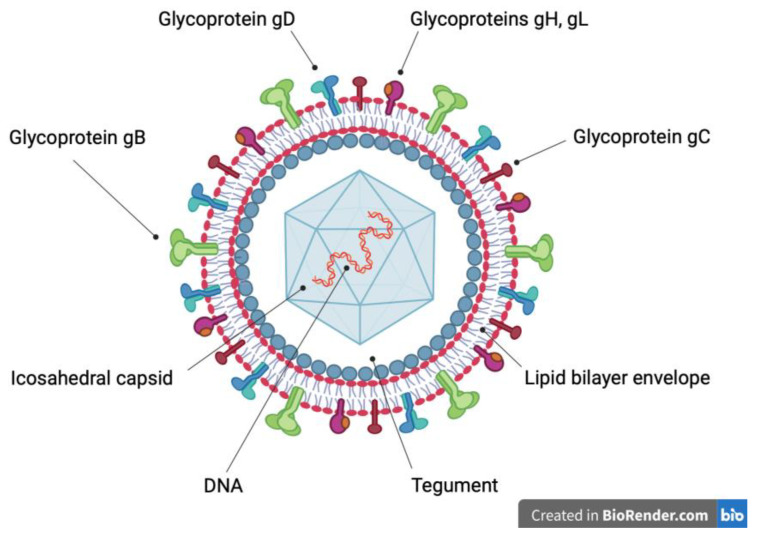
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the herpes virion. A linear, double-strand deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule (red and orange) is surrounded by an icosahedral capsid (light blue), which in turn is covered by tegument (white). The outer surface of the tegument (grey) is associated with a lipid bilayer envelope (red and grey), which contains integral glycoproteins. Glycoprotein B trimer (green), glycoprotein C monomer (brown), glycoprotein D homodimer (light blue), glycoprotein H (purple) and glycoprotein L (orange) heterodimer allow the entry of the virion into the host cell.