Figure 8.
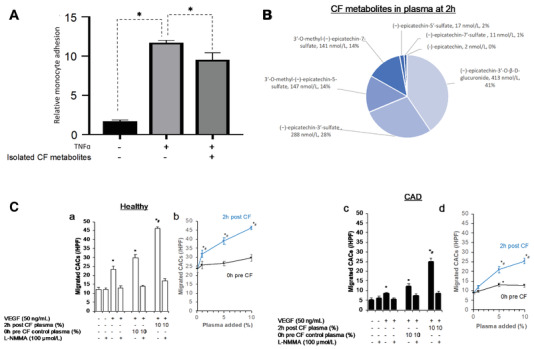
A) Monocytes adhesion after exposure to CF metabolites on endothelial cells in inflammatory condition (n = 9; compared to TNFα at 0.1 ng mL−1 using ANOVA; * p<0.05). B) Profile of CF metabolites in pooled plasma of four healthy volunteers at 2 h after ingestion of 450 mg CF intervention. All metabolites in 0 h pre exposure plasma below limit of detection. C) Effect of post exposure and control plasma on migration of circulating angiogenic cells (CAC) from healthy volunteers (a, b) and patients with coronary artery disease (CAD; c, d) toward a gradient of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in Boyden chamber over 6 h C) Cell migration significantly differed between healthy and CAD and CF plasma dose‐dependently increased chemotaxis in both groups (Cb+d: repeated measurements ANOVA: p interaction interventionxdose <0.001, p interaction interventionxdosexgroup = 0.417). (Ca+c) The increase in chemotaxis but not chemokinesis was inhibited by the eNOS inhibitor L‐NMMA. (Ca+c) * p<0.05 versus no additives, # p<0.05 versus 0h plasma; (Cb+d) * p<0.05 versus 0% plasma, # p<0.05 versus respective 0h plasma; # p<0.05 versus 0h plasma.
