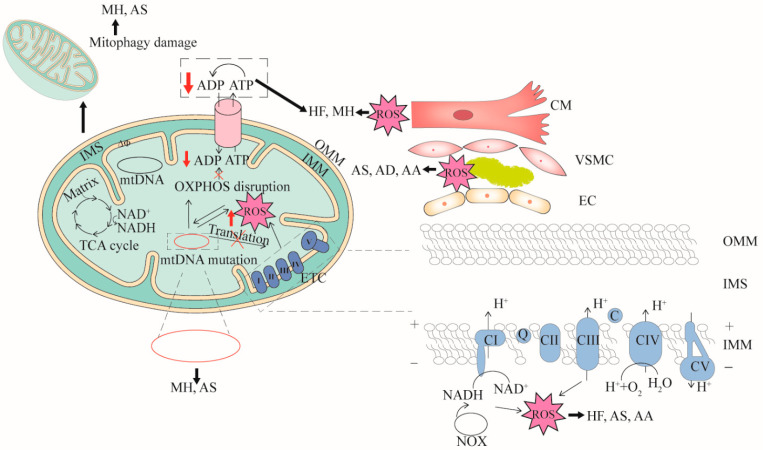
Figure 1.
The relationships between mitochondrial dysfunction and CVDs. Four features (mtDNA mutation, mitophagy damage, decreased OXPHOS and increased ROS) associated with mitochondrial dysfunction are demonstrated. mtDNA mutation can cause dysfunction of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex or cytochrome transcription related to OXPHOS. When OXPHOS is impaired, ATP synthesis is reduced and excess ROS is generated. mtDNA mutation directly affects mitochondrial function or ROS production. In turn, high levels of ROS damage mitochondria. Cardiomyocyte cells (CM), vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), and endothelial cells (EC) that are impaired by mitochondrial dysfunction can cause CVDs. mtDNA mutation can cause myocardial hypertrophy (MH) and atherosclerosis (AS), mitophagy damage can cause MH and AS, decreased OXPHOS can cause heart failure (HF), aortic aneurysm (AA) and AS, and increased ROS can cause AS, aortic dissection (AD) and AA. OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMS, inter membrane space; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane.