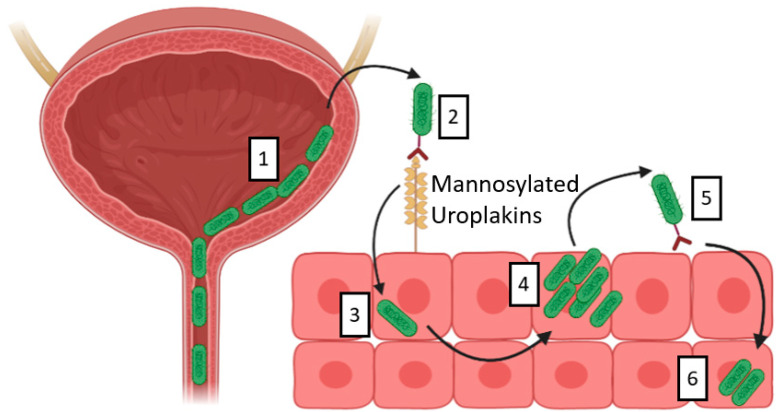
Figure 1.
Proposed model of UPEC-induced UTI. UPEC is thought to ascend the urethra (1) and then bind to mannose residues on uroplakins on the urothelial cell surface (2). Following binding, UPEC is internalised (3). After internalisation UPEC can follow two pathways, either UPEC multiplies within the urothelial cells (4) and then effluxes out to recolonise the bladder (5); or small numbers of UPEC remains in a quiescent state within the host urothelial cells (6) [17].