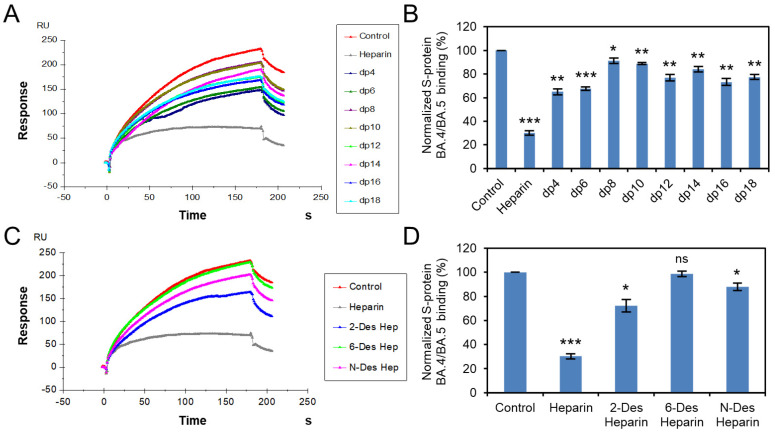
Figure 4.
S protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5)–heparin interaction inhibited by heparin oligosaccharides/desulfated heparins using solution competition. (A) SPR sensorgrams of S protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5)–heparin interaction competing with different heparin oligosaccharides. Concentration of S-protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5) is 250 nM mixed with 1 µM of different heparin oligosaccharides. (B) Bar graphs (based on triplicate experiments with standard deviation) of normalized S-protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5) binding preference to surface heparin by competing with different heparin oligosaccharides. (C) SPR sensorgrams of S protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5)–heparin interaction competing with different desulfated heparins. Concentration of S-protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5) is 250 nM mixed with 1 µM of different desulfated heparins. (D) Bar graphs (based on triplicate experiments with standard deviation) of normalized S-protein RBD (BA.4/BA.5) binding preference to surface heparin by competing with different desulfated heparins. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired two-tailed t-test (ns: p > 0.05 compared to the control, *: p ≤ 0.05 compared to the control, **: p ≤ 0.01 compared to the control, ***: p ≤ 0.001 compared to the control).