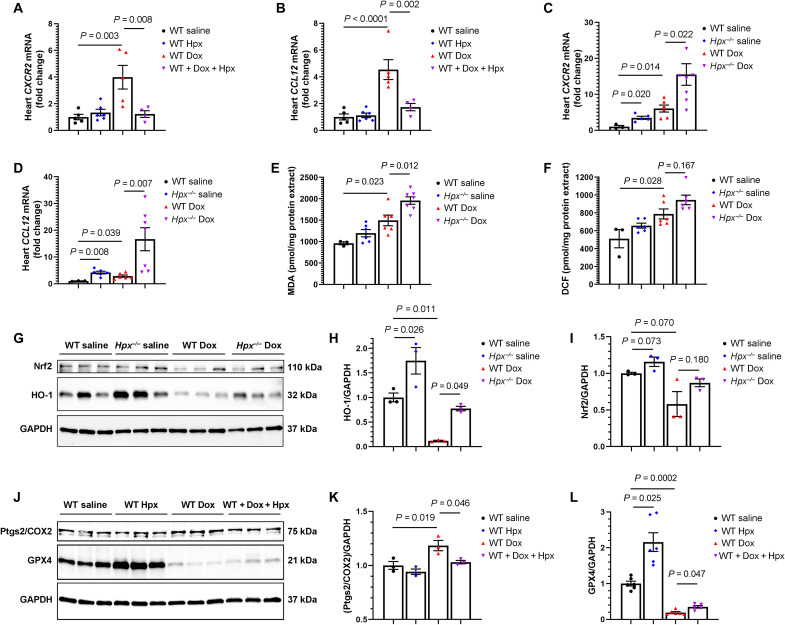
Fig. 7. Hpx modulates Dox cardiac toxicity via suppression of the inflammatory macrophage phenotype and ferroptosis.
(A and B) Cardiac CXCR2 and CCL12 mRNA levels in the heart in WT mice treated with saline (n = 5), Hpx (n = 6), Dox (n = 5), and cotreatment of Dox and Hpx (n = 4). (C and D) CXCR2 and CCL12 mRNA levels in the heart in WT or Hpx−/− mice treated with saline (n = 3 and 6) or Dox (n = 6 and 7). (E and F) Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and DCF fluorescence in the heart in WT or Hpx−/− mice treated with saline (n = 3 and 6) or Dox (n = 6 and 7). (G) Cardiac HO-1 and Nrf2 detected by Western blot in WT or Hpx−/− mice treated with saline or Dox (n = 3 per group). (H and I) Quantification of HO-1 and Nrf2. (J) Cardiac Ptgs2/COX2 and GPX4 detected by Western blot in WT mice treated with saline, Hpx, Dox, and cotreatment of Dox and Hpx (n = 3 per group). (K and L) Quantification of Ptgs2/COX2 and GPX4. GAPDH was used as loading control. All samples were harvested within 24 hours after completion of the 2-week Dox regimen. Data were expressed as means ± SEM. Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey-Kramer test was used to compare the means of experimental groups.