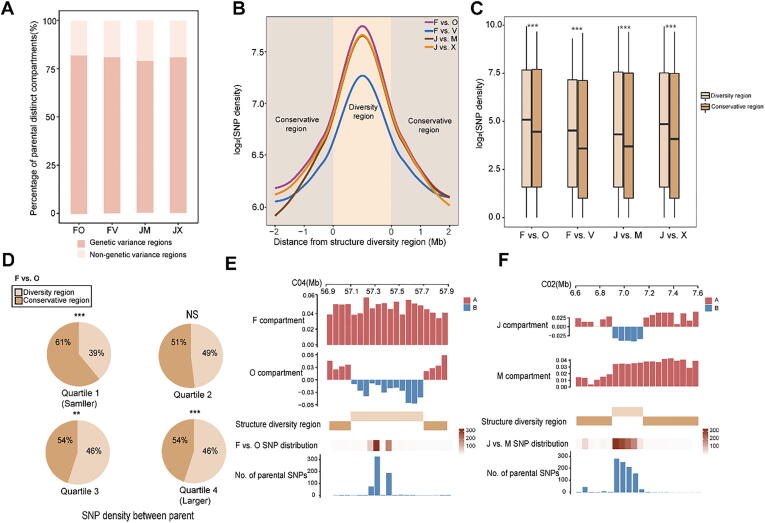
Fig. 3.
Dynamic changes in compartments correlate with genetic variance among parents. A, Distribution of parental distinct compartments among parental genetic variance regions. B, SNP density levels between parents around diversity region borders. Lines show average values across 50-kb bins. C, Distribution of SNP density between diversity regions and conservative regions. ***P < 0.001 (Wilcoxon rank-sum test.). D, Percentages of F-O-FO diversity regions and conservative regions with SNP density classifications. According to the analysis of SNP density order between parents, quartile 1 is smaller and quartile 4 is larger. ***P < 0.001; NS, no significant difference (Fisher’s exact test). E and F, Example of the relationship between diversity/conservative regions and SNP density in parents. The two upper tracks show the features of compartments in the parents: red, A; blue, B. The middle track shows the distribution of diversity regions and conservative regions. The two lower tracks show the distribution of different SNPs between parents and the number of SNPs. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)