Figure 2. Influence of genetic variants on GSDMB-mediated non-lytic activity.
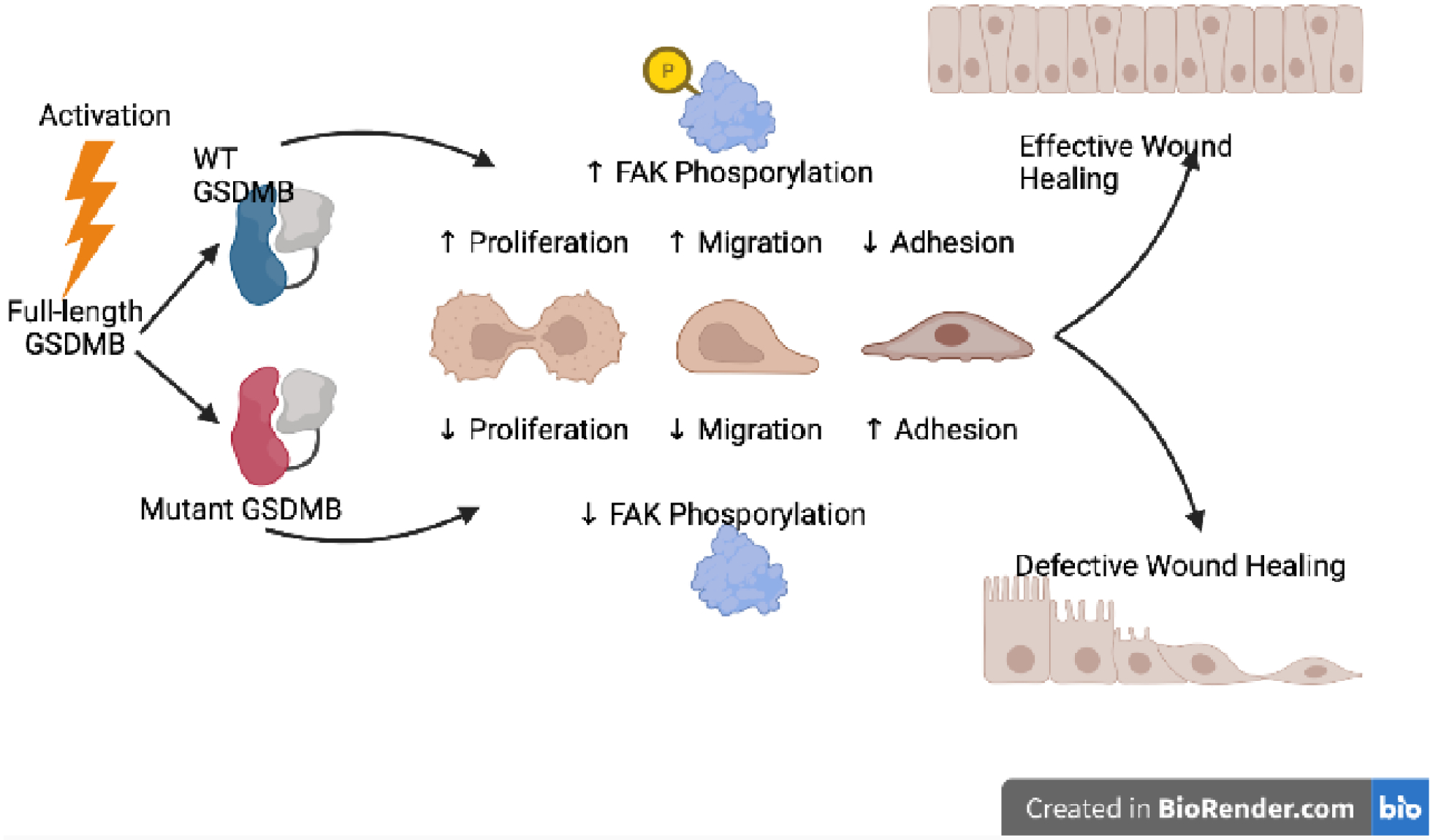
Activation of full-length GSDMB promotes translocation to the plasma membrane of IECs, and increased proliferation and migration, and decreased extracellular matrix adhesion that facilitates epithelial restitution and repair, and overall efficient wound healing. GSDMB-mediated FAK phosphorylation is thought, at least in part, to mechanistically underlie these processes. Conversely, mutant GSDMB, as a consequence of carriage of disease-associated GSDMB variants, results in decreased FAK phosphorylation, which interferes with proliferation, migration and adhesion processes, with an overall impairment of epithelial barrier function and appropriate wound healing. FAK, focal adhesion kinase; WT, wild-type.
