Figure 4. AGO adopts distinct conformations when engaged with canonical or TDMD-inducing targets.
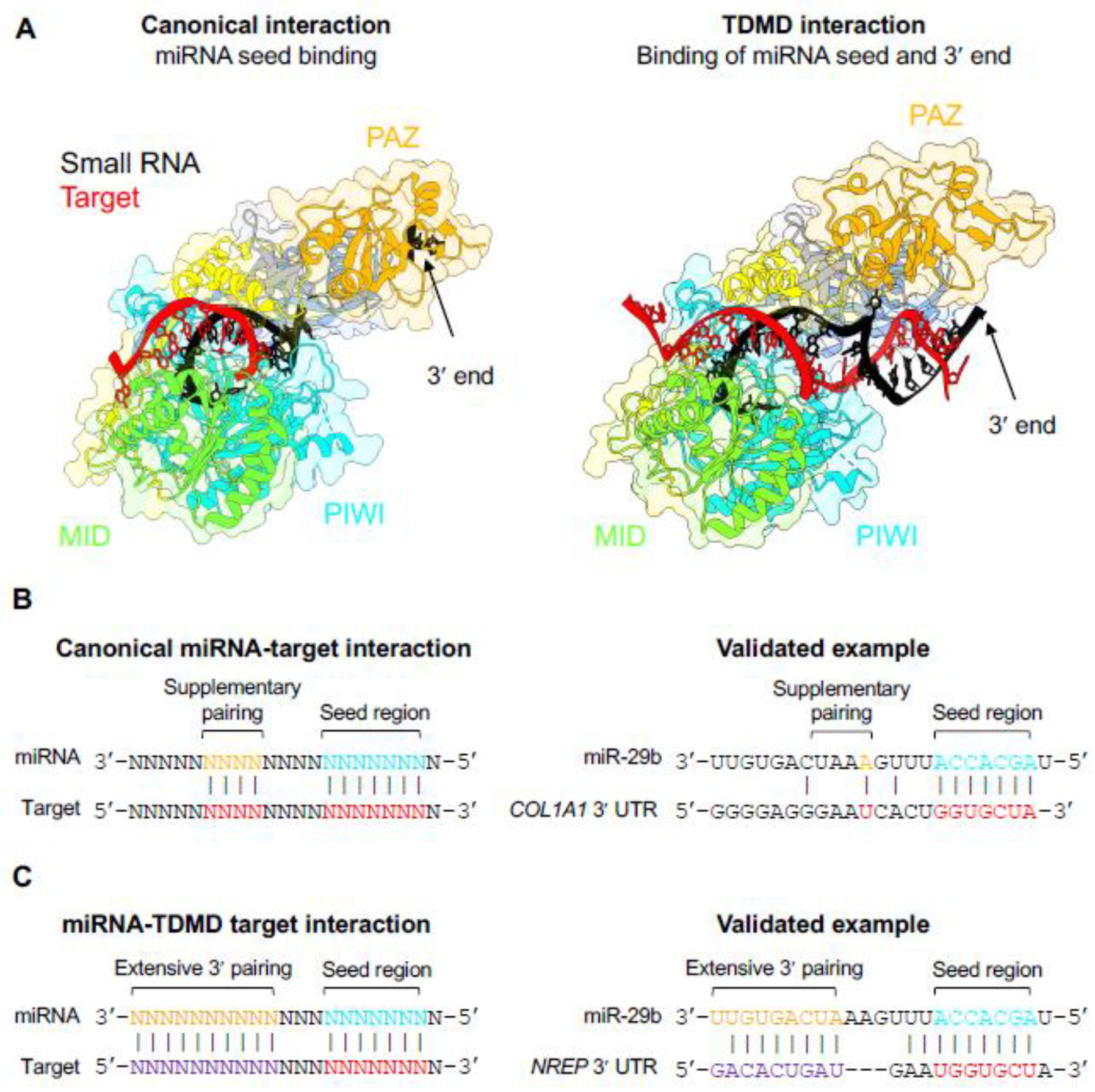
(A) When bound to a canonical target via base-pairing of the seed region, the miRNA 3′ end is buried in the PAZ domain of AGO (left panel; PDB: 4W5T) [10]. Interaction with a TDMD-inducing target with extended 3′ complementarity, however, exposes the miRNA 3′ end to solvent, which enables tailing and trimming (right panel; PDB: 6MDZ) [72]. Protein structures were rendered by UCSF ChimeraX [109]. (B) Canonical miRNA-target interactions involve base-pairing of the miRNA seed region with or without additional supplementary pairing [1]. A validated canonical binding site for miR-29b in the 3′ UTR of human COL1A1 is shown [110]. (C) Targets that induce TDMD base pair with the miRNA seed region, display extensive complementarity to the miRNA 3′ end, and have central mismatches. Interaction of miR-29b with a TDMD-inducing site in the 3′ UTR of human NREP is shown [82].
