Fig. 1.
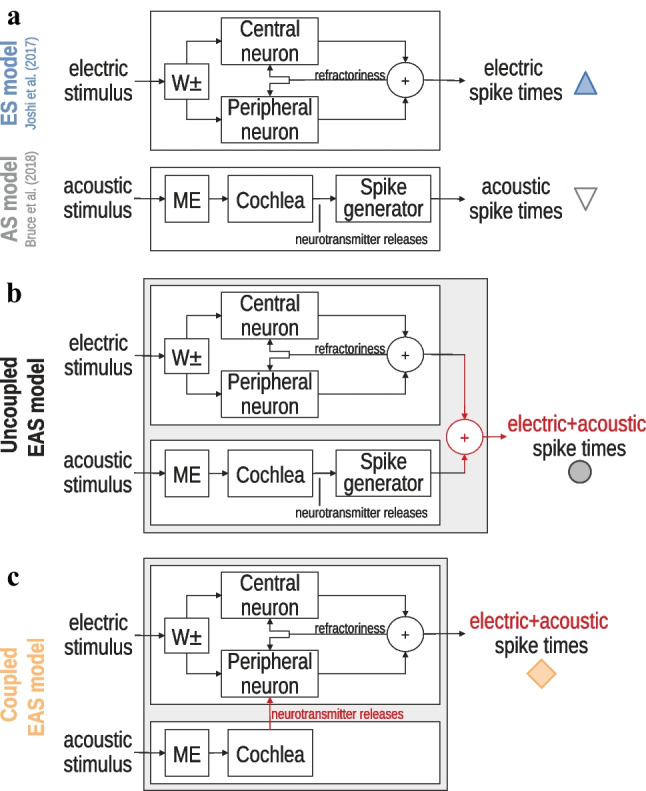
Block diagrams for the used models. The input to each model is the waveform of an electric or acoustic stimulus or a combination of both and the output is an array of spike times in the ANF. The symbols indicated next to each model output are used in the results section to represent the respective model results. a Top: extended ES model based on Joshi et al. [42], bottom: AS model of Bruce et al. [35]. b Uncoupled EAS model without interaction. c Coupled EAS model: the neurotransmitter release events from the acoustic IHC model trigger an additional excitatory input current to the peripheral neuron of the ES model, bypassing the acoustic spike generator. W ± – stimulus weighting block, Central/peripheral neuron—adaptive integrate-and-fire point neuron models with sub- and suprathreshold feedback currents; ME—middle ear filter; Cochlea—includes basilar membrane, outer hair cells, inner hair cells, and the synapse; Spike generator—generates spikes by accounting for the refractoriness of the ANF
