Figure 2. 5-HTR6-primary cilia are in contact with serotonergic axonal varicosities.
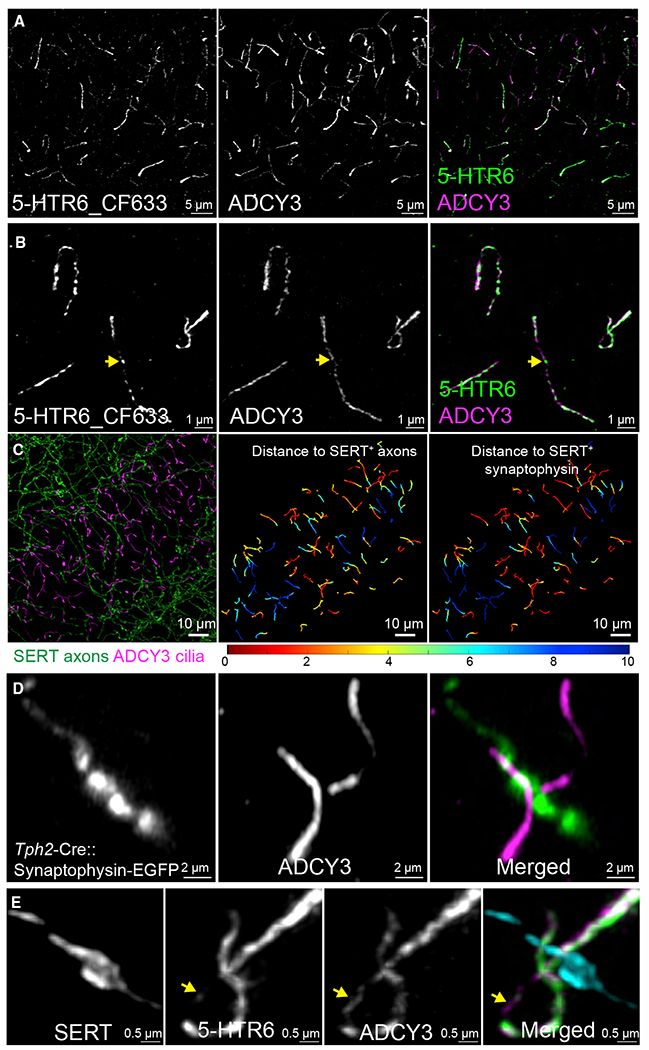
(A) HTR6 (labeled by CF633, green in merged panel) is highly enriched in CA1 neuronal primary cilia (ADCY3, magenta in the merged panel: 20 μm MIP).
(B) Magnified images from (A). 5-HTR6s are not evenly distributed along the length of cilia and can be enriched at areas with low ADCY3 labeling (arrow).
(C) Left panel: cilia (magenta) co-labeled with serotonergic axons (green). 20-μm maximum intensity projection (MIP). Middle panel: cilia in the left panel color coded by the shortest distance to a serotonergic axon. Right panel: cilia from left panel color coded with the shortest distance to a serotonergic axon-associated synaptophysin punctum.
(D) Floxed synaptophysin-EGFP driven by Tph2-Cre showed ADCY3-labeled cilia (magenta in the merged panel) in contact with serotonergic presynaptic terminals (amplified by anti-GFP and Alexa 488, green in the merged panel).
(E) 5-HTR6 (green in the merged panel) are enriched on the cilia at the axonal contact sites (SERT, cyan in the merged panel). Two cilia are in contact with a single serotonergic axonal varicosity. ADCY3 (magenta in the merged panel) can extend beyond the contact site that has few 5-HTR6 (arrow).
(A), (B), and (E) are deconvolved confocal images with photon counting detection (Leica). (C) and (D) are Airyscan images (Zeiss). Data from 3- to 4-month-old male C57BL/6J mice.
