Figure 6. 5-HTR6 signaling modulates H4K5 acetylation.
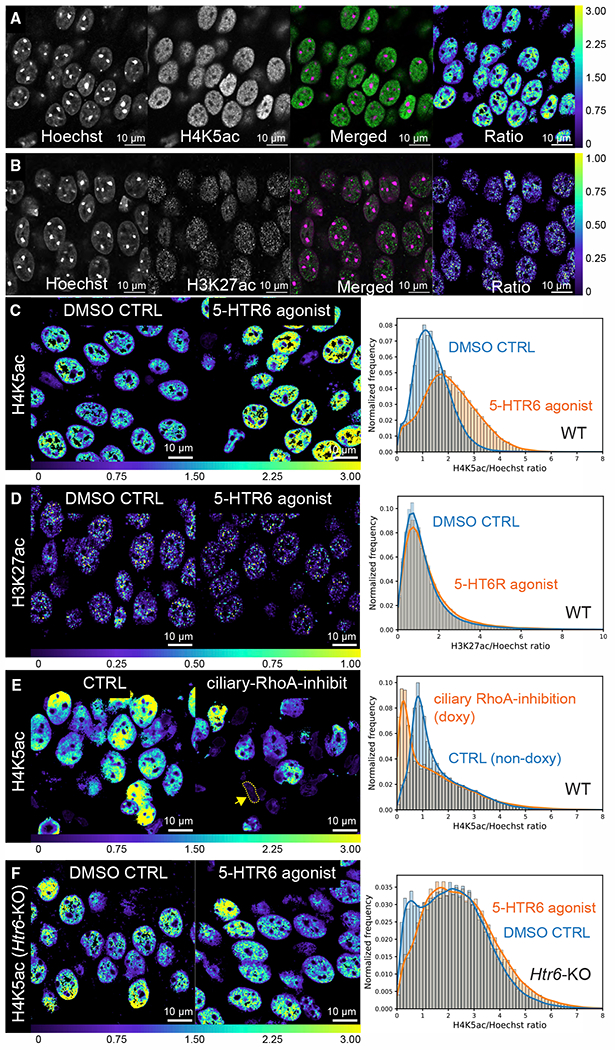
(A and B) Ratiometric measurements of H4K5ac (A) and H3K27ac levels in fixed mouse brain sections (B). Monoclonal antibodies against H4K5ac and H3K27ac were used to detect histone lysine acetylation (single Airyscan optical sections; green, merged panel). The fluorescent intensity is divided by the Hoechst intensity levels (magenta in the merged panel) to obtain the ratio (rightmost panel, downsampled).
(C) 5-HTR6 agonist stimulation increases H4K5ac level. ~60% increase in mode: DMSO: 1.10, WAY181187: 1.76.
(D) 5-HTR6 stimulation did not significantly alter H3K27ac level: modes of DMSO and WAY181187 are both 0.77.
(E) Ciliary RhoA inhibition for ~1-week decreases H4K5ac level; ~68% decrease in mode: CTRL: 0.82, doxy: 0.26. Many nuclei have small and irregular shapes (arrow).
(F) 5-HTR6 agonist stimulation in Htr6 KO mice does not increase the H4K5ac level. ~24% decrease in mode: DMSO: 2.16, WAY181187: 1.73.
(C–F) Left and middle panels: single optical sections of the H4K5ac/Hoechst or H3K27ac/Hoechst ratio. Right panel: histograms with kernel density estimates from entire stacks. Data in (A)–(D) were from 3- to 3.5-month-old and (E) and (F) from 4-month-old male C57BL/6J mice.
