Figure 2. CFE synthesized FL SUN proteins are incorporated into SUPER templates via a potential fusion-based mechanism.
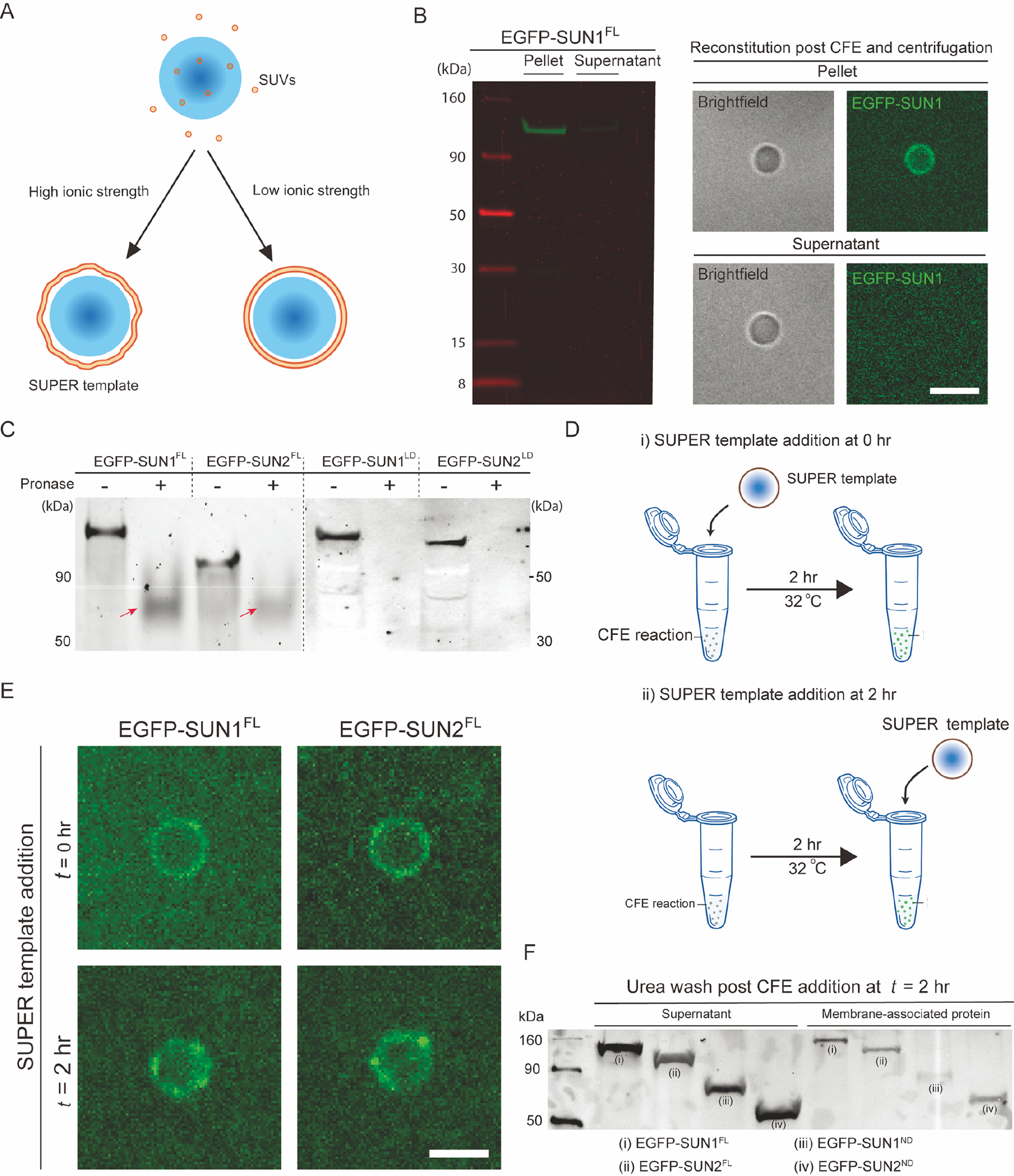
A) Schematic depicting the formation of supported lipid bilayers on silica beads in the presence or absence of low or high ionic strength buffers. As shown, SUPER templates are typically created when the fusion of SUVs results in the formation of loosely bound unilamellar membranes under high salt conditions. B) In-gel fluorescent image of pellet and supernatant fractions of a CFE reaction with SUN1-EGFP. The pellet and supernatant fractions were isolated using the Airfuge fractionation assay and subsequently added to SUPER templates for imaging (right) or directly run on gel (left). Scale bars: 5 μm. C) In-gel fluorescence image of CFE reactions expressing the indicated EGFP-tagged proteins that were or were not exposed to pronase. Arrows: Incompletely pronase-digested proteins. D) Schematic illustrating how the ability of EGFP-tagged FL SUN proteins to be reconstituted in SUPER templates added at the start of the CFE reaction (i) or 2 hours after its initiation (ii). The SUPER templates were washed in 1X PBS with 6M urea before imaging. E) Representative confocal fluorescent images of SUPER templates added to the indicated EGFP-tagged SUN protein CFE reactions at the indicated time points. Scale bars: 5 μm. F) Western blot of the bulk CFE supernatant and membrane-associated protein fractions of CFE reactions to which SUPER templates were added 2 hours after initiating the synthesis of the indicated EGFP-tagged SUN protein constructs, as described in panel D(ii). The supernatant and membrane-associated fractions represent SUN proteins in bulk CFE reactions and SUPER templates, respectively.
