Figure 16.
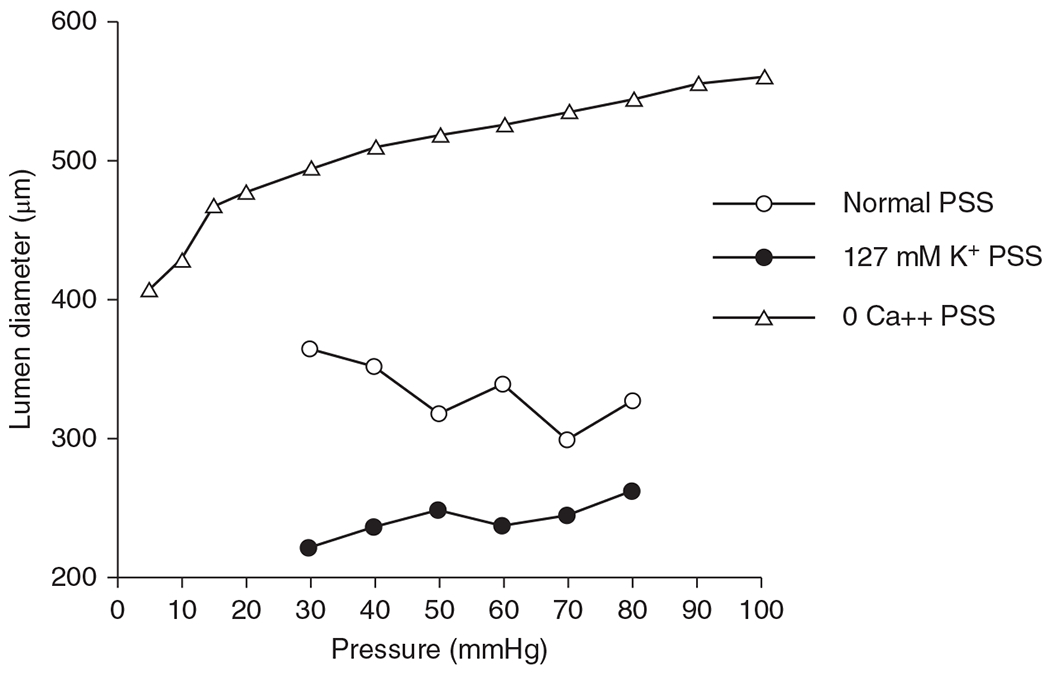
Pressure-diameter relationship of human infant middle cerebral artery at 37 week gestation. The artery was subjected to changes in transmural pressure in random steps between 30 and 80 mmHg in physiologic salt solution (PSS). With increased transmural pressure, arterial diameter decreased (open circles), indicative of increased myogenic tone. In the presence of PSS containing 127 mmol/liter of KCl to induce depolarization and a maximum contractile state (closed circles), diameter increased slightly with increasing transmural pressure. In the presence of Ca2+-free PSS containing 2 mmol/liter EGTA (triangles), the diameter increased passively at each pressure value. The difference between the passive and active curves indicates that the human middle cerebral artery is capable of generating a considerable myogenic response at this developmental age. Source: Adapted, with permission, from Bevan RD, et al., 1998 (58), © 1998, Springer Nature.
