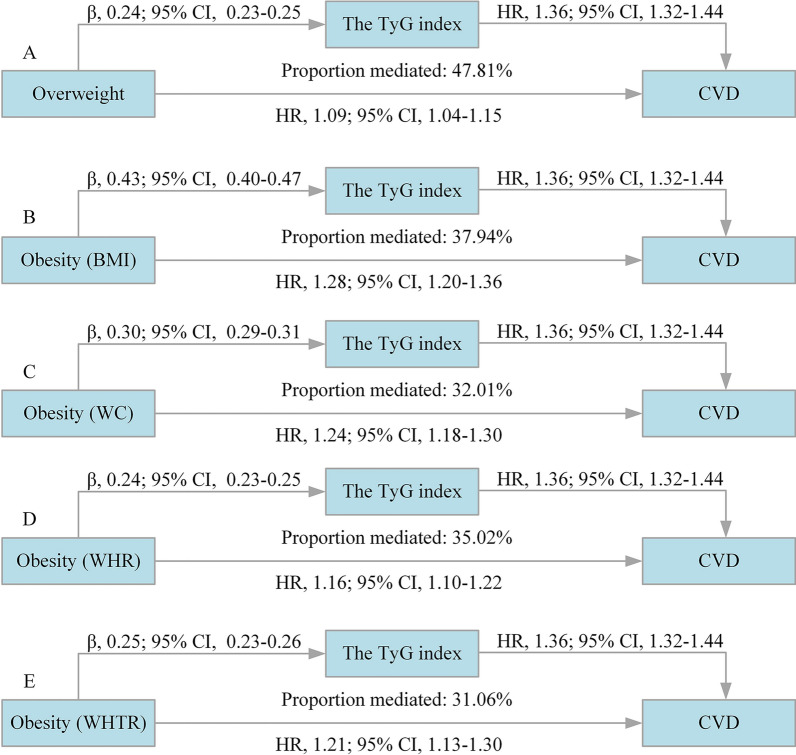
Fig. 2.
Decomposition of the total association of general and central obesity and the risk of CVD into direct and indirect associations mediated by the TyG index. BMI body mass index, CI confidence interval, CVD cardiovascular disease, HR hazard ratio, TyG triglyceride-glucose index, WC waist circumference, WHR waist circumference to hip ratio, WHTR waist circumference to height ratio. Compared with normal weight participants for general obesity and WC < 90 cm in men or < 85 cm in women, WHR < 0.90 in men or < 0.80 in women, and WHTR < 0.60 as a reference for central obesity. All models were adjusted for age, sex, education, income, smoking status, drinking status, history of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, antihypertensive agents, antidiabetic agents, lipide-lowering agents, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein