FIGURE 1.
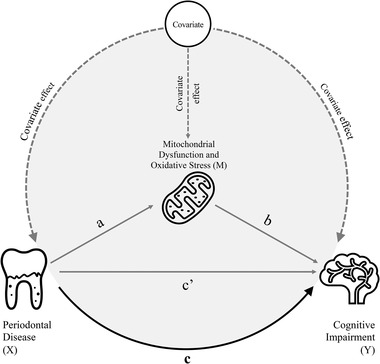
Theoretical diagram of the mediation model for the association between periodontal disease (exposure) and cognitive impairment (outcome) with the biomarker of mitochondrial dysfunction or oxidative stress as a mediator. Path a: regress “mediator (M)” on “exposure (X)” to examine if “exposure (X)” is a significant predictor of the “mediator (M).” If not, then it is unlikely to mediate anything. Path b: regress “outcome (Y)” on “mediator (M)” to test if the “mediator (M)” is significantly associated with “outcome (Y).” If not, then it is unlikely to mediate anything. Path c: regress “outcome (Y)” on “exposure (X)” to test if the “exposure (X)” is significantly predictor of “outcome (Y)” (total effect). Path c': regress “outcome (Y)” on both “exposure (X)” and “mediator (M)” to test if “mediator (M)” is a significant predictor of “outcome (Y)” and to observe whether the association between “exposure (X)” and “outcome (Y)” is attenuated when the “mediator (M)” is included (direct effect)
