FIGURE 4.
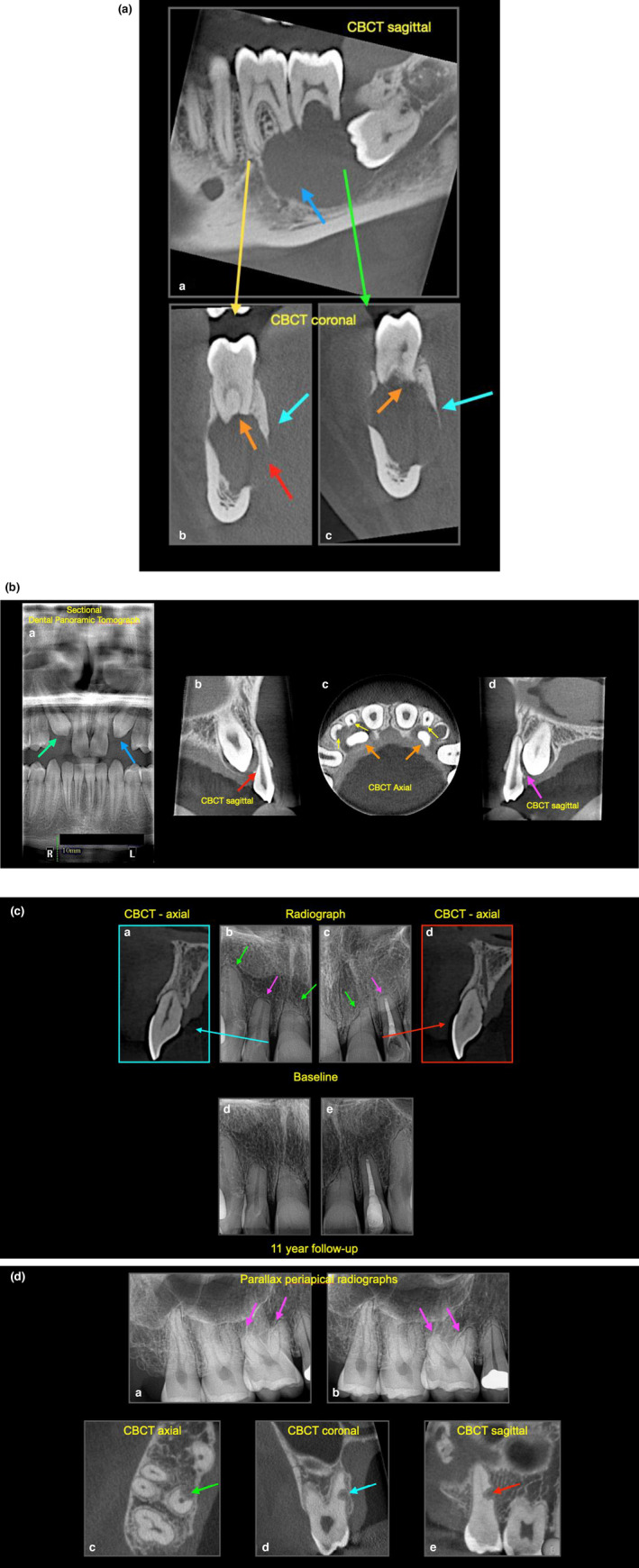
(a) External surface resorption. (a) Sagittal CBCT revealing radiographic large radiolucent lesion (blue arrow) associated with the lower left molar teeth, (b, c) coronal CBCT views revealing significant resorption of the apices of teeth 36 and 37 (orange arrows), expansion (cyan arrows) and perforation (red arrow) of the cortical plate. Note that the periodontal ligament space has disappeared. The lesion was surgically managed and subsequently confirmed to be an ameloblastoma after histological evaluation. (b) External surface resorption. (a) Sectional panoramic of a patient with unerupted, impacted canines (green and blue arrows), (b) sagittal CBCT reveals the 13 is impacted on the 12 resulting in ESR, and disappearance of the periodontal ligament in this region, (c) axial CBCT view reveals the extent of ESR (yellow arrows) associated with the impacted canines (orange arrow), (d) sagittal CBCT reveals the 23 is also impacted on 22. (c) External surface resorption (a– d) baseline radiographic images of a 45‐ year‐ old patient with history of 4‐ year fixed bracket orthodontic treatment. Radiographs show clear evidence of ESR, note the different presentations; teeth 12, 13, 22 have blunted apices, whereas teeth 11, 21 have more angular ESR, this may be due to the direction of orthodontic forces applied, (d–e) 11‐year follow up shows that all the teeth are heathy, note that the periodontal ligament space is visible. (d) External surface resorption and external replacement resorption. (a) Parallax periapical radiographs of upper right molars region taken to assess the degree of external surface resorption (pink arrow) on tooth 16 after a rapid course of orthodontics, fixed braces were placed from 16 to 26, the 27 and 28 were not used for orthodontic anchorage. (c–e) CBCT slices reveal an unusual presentation of external replacement resorption of the 17, the orthogonal views reveal the well‐defined resorptive defect, which is very close proximity to the root canal—no active treatment was advised, instead the patient was advised to attend for annual reviews (watchful waiting), including sensitivity testing and radiographic assessment. Note that the periodontal ligament space is visible
