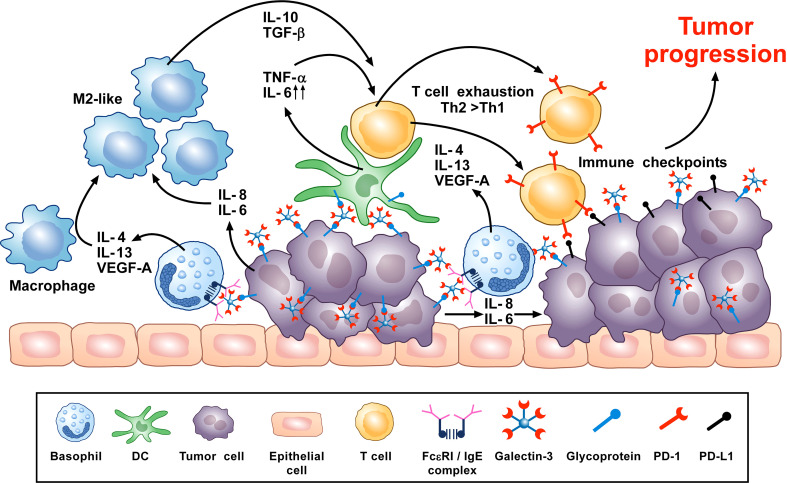
Figure 3.
Theoretical representation of how basophils can promote tumor progression. Galectin-3 (Gal-3) is a lectin highly expressed by many types of cancer cells, frequently manifesting as a marker of poor prognosis with capacity to mediate immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment (TME) (266). Recent in vitro studies show that Gal-3, expressed by the A549 adenocarcinoma cell line (or EC-Gal-3), has the capacity to activate basophils to secrete copious amounts of IL-4/IL-13 (16, 223). Both cytokines are known to promote M2-like macrophages, which are major players in the TME (227, 263–265). IL-4-producing basophils have been identified in the TME of human pancreatic cancer, with mouse models indicating that this IL-4 promotes a Th2>Th1 response that is more conducive to tumorigenesis (80). Additionally, basophils are long known to secrete VEGF-A (64) that promotes angiogenesis. Other studies show that basophils can induce IL-6/IL-8 secretion from cell lines through a mechanism requiring cell-to-cell contact (283) (JTS, unpublished). This tumor cell-derived IL-6/IL-8 is implicated in playing a critical role in metastasis formation (284). Likewise, dendritic cells and monocytes activated by EC-Gal-3 are shown to produce high levels of TNF-α/IL-6 in vitro (285). Chronic production of these cytokines, when combined with M2 cell-derived IL-10/TGF-β, are implicated in promoting T-cell exhaustion by up-regulating checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., PD-1) that interact with tumor cell-associated markers (PD-L1) to suppress cytotoxic T cell activity (286). V-domain immunoglobulin suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) is another immune checkpoint receptor which plays a role in cancer progression (287, 288) and regulates allergen-specific Th2-mediated immune responses (289). Overall, it is proposed that the combined actions of these dysregulated innate immune responses synergize to promote tumorigenesis.