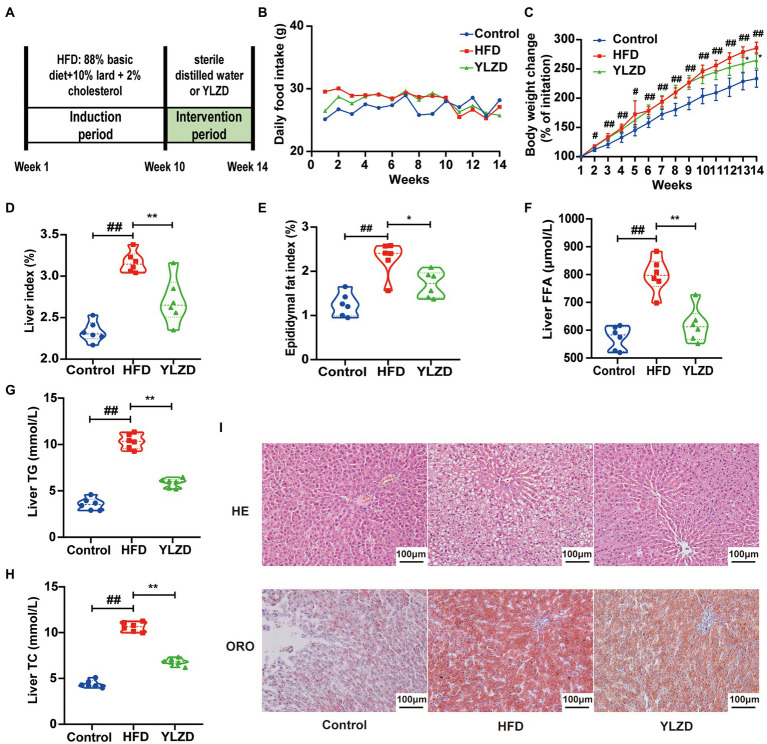
Figure 1.
YLZD improved the general status and mitigated hepatic lipid deposition. (A) Experimental design, (B) daily food intake, (C) body weight change, (D) Liver index = Liver weight/Body weight × 100, (E) Epididymal fat index = Epididymal fat weight/Body weight × 100, (F–H) The level of liver FFA, TG and TC, respectively, and (I) Representative images of HE and oil red staining livers (magnification, ×200). Control group, normal rats treated with distilled water; HFD group, HFD-induced liver injury rats treated with distilled water; YLZD group, HFD induced liver-damaged rats treated with YLZD 1.92 g/kg/day for 4 weeks. Values are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 6 rats/group). ##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 versus the Control group; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 versus the HFD group.