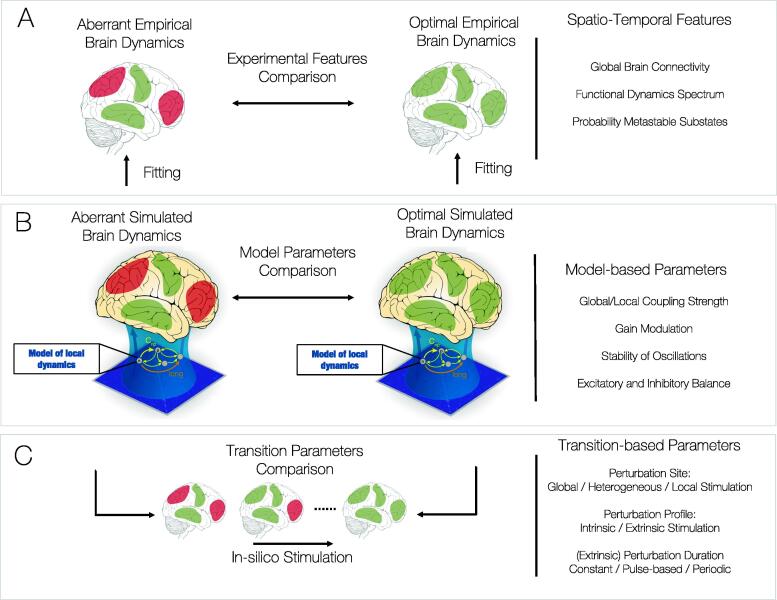
Fig. 1.
Conceptual Overview of Dynamic Sensitivity Analysis A) Descriptive Analysis. Traditional statistical analysis between empirical fMRI brain recordings of different study groups (example control and patient groups). Dynamics can be described by various features across space and time, for example Global Brain Connectivity, Functional Dynamics Spectrum or Probability Metastable Substates (PMS). B) Explanatory Analysis. Generative modelling approaches to describe the emergent dynamics of coupled dynamical units in the brain network. Network models can be adjusted to approximate spatio-temporal features of brain dynamics at the individual or group-level by tuning model parameters relating to various brain mechanisms, such as global/local coupling strength, gain modulation, stability of oscillations or excitatory/inhibitory balance. Relating to different brain mechanisms, these parameters can subsequently be statistically compared between conditions to obtain model-based features characteristic of each brain state. C) Predictive Analysis. The framework of Dynamic Sensitivity Analysis consists in the systematic investigation of the optimal strategy promoting a transition between distinct brain states. This framework provides a non-invasive means to evaluate the nonlinear response of distinct perturbation strategies aimed at promoting a transition from an aberrant brain state to an optimal and healthy brain state.