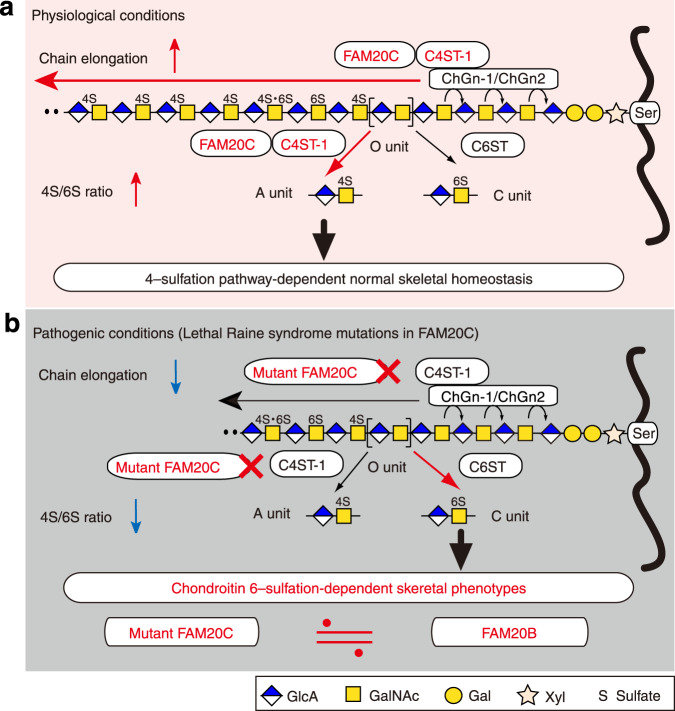
Fig. 6. Non-enzymatic functions of FAM20C in the control of CS biosynthesis and its involvement in Raine syndrome etiology.
In physiological states (a), FAM20C can physically interact with C4ST-1 and augment the enzymatic activity of C4ST-1, leading to increased length of the individual CS chains via cooperative actions with glycosyltransferases (N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases; ChGns)20,33 and to an elevated 4S/6S ratio. In contrast b, lethal Raine syndrome mutations in FAM20C cause functional uncoupling between FAM20C and C4ST-1, perturbing the C4ST-1-mediated chain elongation process and sulfation balance of CS chains. The consequent decrease in the 4S/6S ratio may be involved in the manifestation of chondroitin 6-sulfation-dependent skeletal phenotypes, which might be recapitulated by a gain-of-function of FAM20B.