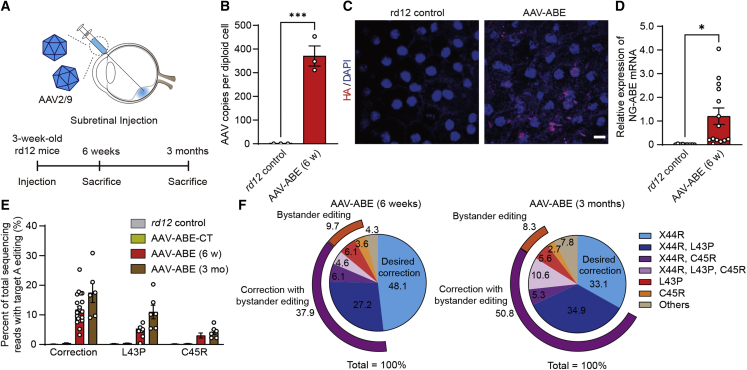
Figure 3.
Comprehensive analysis of in vivo adenine base editing to correct a nonsense mutation in the RPE of rd12 juvenile mice
(A) A schematic diagram depicting the design of animal experiments. (B) Quantitation of AAV copies per diploid cell of the RPE at 6 weeks after subretinal injection of AAV-ABE in 3-week-old rd12 mice (n = 3). (C) Representative photographs of confocal microscopy of the RPE of rd12 mice at 6 weeks after subretinal injection of AAV-ABE. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Quantitation of relative NG-ABEmax mRNA expression in the RPE at 6 weeks after subretinal injection of AAV-ABE in 3-week-old rd12 mice (n = 9 and 14 for each group). (E) Quantitation of the intended A to G correction at position 6 (A6) in the RPE at 6 weeks (AAV-ABE (6 w)) and 3 months (AAV-ABE (3 mo)) after subretinal injection of AAV-ABE in 3-week-old rd12 mice (n = 11, 8, 21, and 6 for each group). AAV-ABE-CT, rd12 mice receiving one AAV vector containing the C-term part of NG-ABEmax. (F) The editing outcomes including the intended (X44R) and bystander edits in RPE cells at 6 weeks and 3 months after subretinal injection of AAV-ABE in 3-week-old rd12 mice (n = 21 and 6 for each group). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t test.