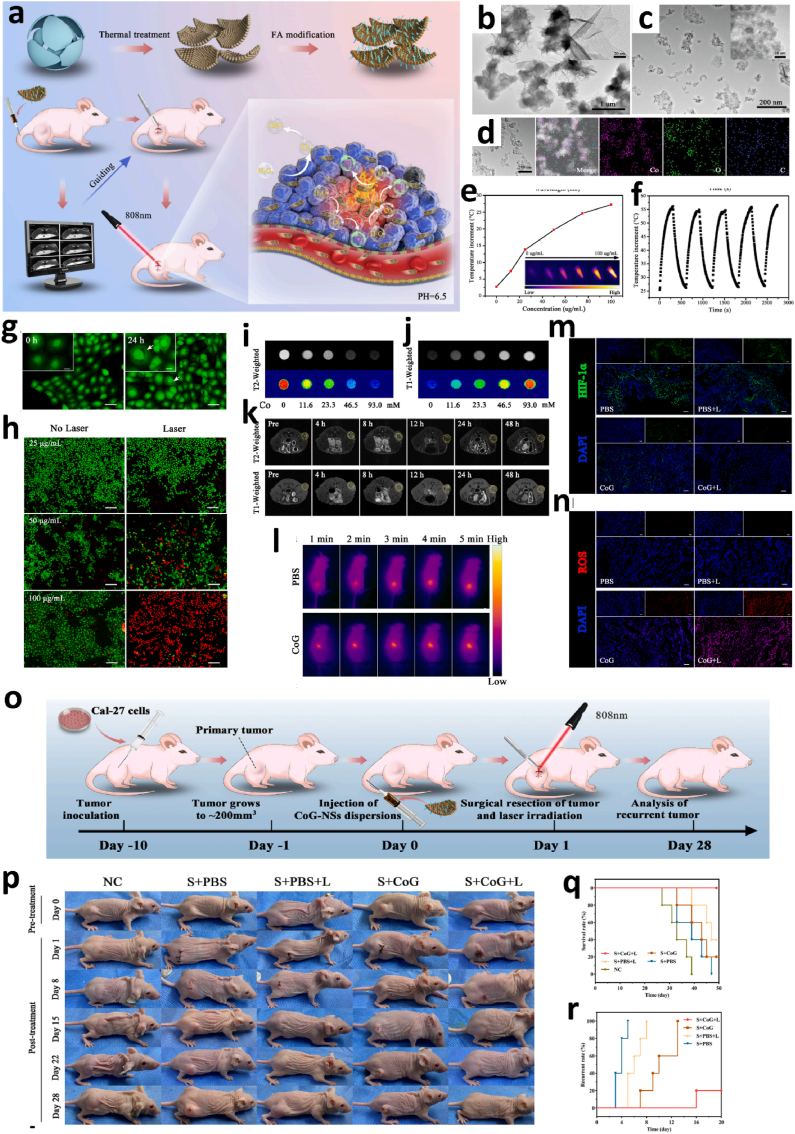
Fig. 6.
CoG-NS-mediated MR-guided neoadjuvant phototherapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma. a. Scheme of the synthesis of CoG-NSs and its MR-guided preoperative phototherapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma. b. TEM image of CoG-FSs. c. TEM image of CoG-NSs. d. Elemental mapping of CoG-NSs (EDS). e. Concentration dependent photothermal effect of CoG-NSs. f. Photothermal stability of CoG-NSs over laser on/off cycles. g. Uptake of CoG-NSs by CAL-27 cells (scale bar: 20 μm). h. Live/dead cells staining of CAL-27 cells with Calcein–AM (green: live cells) and PI (red: dead cells) after treatment with various concentration of CoG-NSs with or without laser (scale bar: 100 μm). i. Phantom T2-weighted MR images of different concentrations of CoG-NSs suspensions. j. Phantom T1-weighted MR images of different concentrations of CoG-NSs suspensions. k. In vivo axial T1 and T2 MR imaging of tumor at different time point post injection of CoG-NSs. l. In vivo infrared photothermal imaging of CAL-27 tumor. m. Immunofluorescence of HIF-1a expression in the tumor after different treatments (scale bar: 100 μm). n. DHE staining of ROS in tumor tissue in different groups (scale bar: 100 μm). o. The schedule of CoG-NS-mediated MR-guided neoadjuvant photo-therapy anticancer recurrence. p. Representative photos of CAL-27 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice in different treatment groups at different time. q. Survival curve of CAL-27 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice in different treatment groups. r. The recurrence of CAL-27 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice in different treatment groups [139]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier.