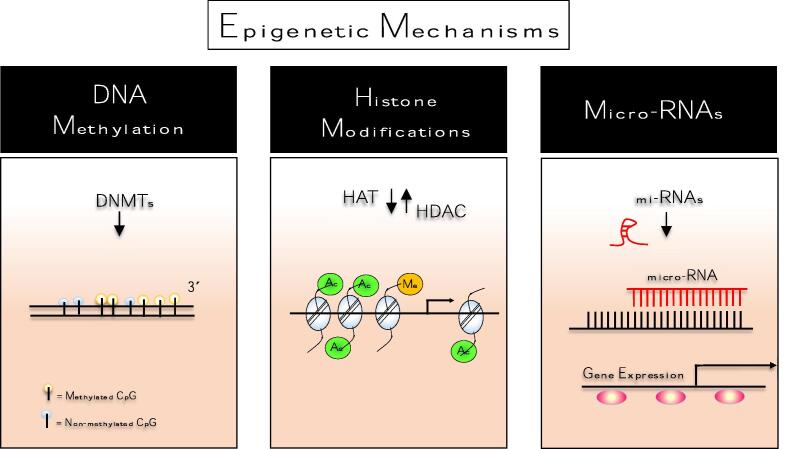
Fig. 2.
Schematic mechanism of epigenetic regulation. Epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression, involving structural changes in chromatin regardless of changes in the DNA sequence. In general, epigenetic mechanisms act to change the accessibility of chromatin for transcriptional regulation by modifications of the DNA and by nucleosome modification or rearrangement from parental to daughter cells. There are three major mechanisms of epigenetic regulation includes (1) DNA cytosine methylation; (2) chromatin remodeling, mostly achieved via histone modification such as methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination, or incorporation of histone variants, and (3) small non-coding RNA (miRNAs) regulation. Epigenetic modifications may be reversible and occur naturally in normal development, health as well as in aging or NCDs development once several factors including environmental factors, lifestyle, upbringing, or emotions may interfere with its regulation. Below is a brief overview of the concept of epigenetic mechanisms. DNA methylation: is defined as a covalent linkage of methyl groups on the C5 position of cytosine residues in DNA, typically in CpG context, catalyzed by DMNTs enzymes using a SAM donor. Histone modifications: refer to covalent post-translational modifications of N-terminal ((including acetylation, phosphorylation, methylation, and ubiquitination) tails of four core histones (H3, H4, H2A, and H2B. Among these alterations, histone acetylation and methylation have received prominence. They are regulated by two groups of enzymes: HAT and HDAC, respectively. The HAT/HDAC system plays a key role in modifying the chromatin structure, which is directly related to the control of the transcriptional process and the gene expression. miRNA: induce degradation of targeted mRNAs by sequence-specific base pairing towards their 3́unstranslated regions within the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) which further inhibits the translation. CpG,cytosine-phosphate-guanine; DNMT,DNA methyltransferase;HAT,histone acetyltransferase;HDAC,histone deacetylase;mi-RNA,micro RNA;SAM,S-adenosyl-methionine.