Figure 1.
TC mutants maintain normal expression of the three constitutive γC-type isoforms
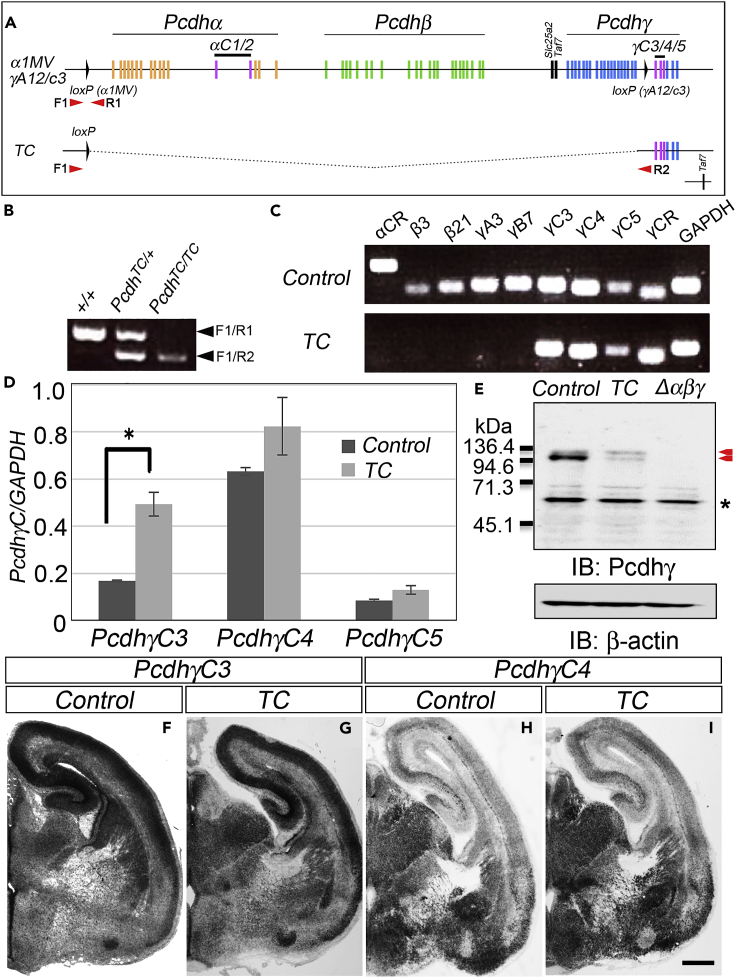
(A) Genetic organization of the TC mutant allele. The genomic positions of α1MV loxP and γA12/C3 loxP insertion sites (upper diagram, see also Figure S1). TC mutants were generated by Cre-induced miotic recombination at α1MV and γA12/C3 loxP sites (lower diagram). Arrows indicate primer positions used for genotyping.
(B) PCR genotyping to distinguish between wild-type (+/+) and TC mutant alleles.
(C) RT-PCR analysis showing the expression of γC3, γC4, and γC5 but not the other isoforms in the deleted clusters. αCR and γCR indicates constant region of Pcdhα and γ, respectively.
(D) Quantitative real-time PCR showing the comparable expression of the three γC-type isoforms to control mice (+/+:TGtaf7), although an increase in γC3 expression was noted. N = 3 animals per genotype. Error bars represent SEM ∗p < 0.05 by t-test.
(E) Western blot detection of Pcdhγ isoforms in E18.5 brain lysates from TC mutants by the antibody against the constant region of Pcdhγ (anti-γCR, indicated by red arrowheads). cPcdh-null mutants (Δαβγ) did not express Pcdhγ, whereas TC mutants exhibited a large reduction but still detectable expression from the remaining γC3, γC4, and γC5 loci.
(F-I) In situ hybridization with a γC3 (F, G) or γC4 (H, I) cRNA probe on coronal sections of E18.5 control (F, H) or TC mutant (G, I) brain. Scale bar: 500 μm.