Figure 1.
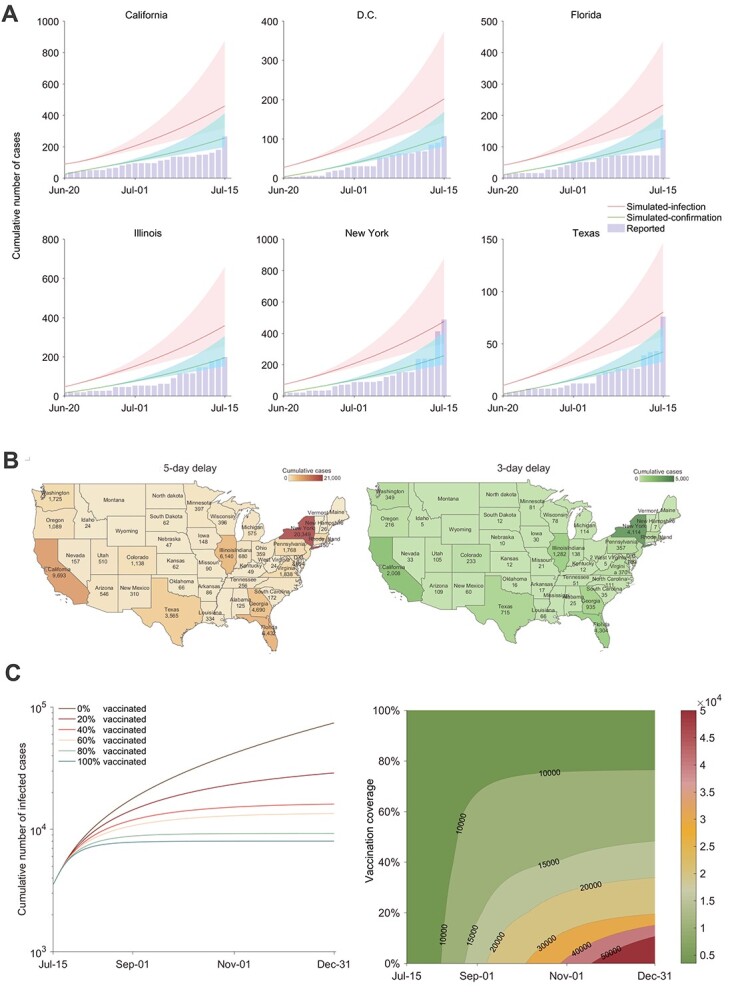
Retrospective simulation of the monkeypox outbreak in the USA, and assessing the impact of rapid diagnosis and ring vaccination on curbing monkeypox spread. (A) Model simulation to fit the spread of MPXV in some representative states of the USA from 20th June to 15th July. The model considers an average delay of 9 days from disease onset to laboratory confirmation in the early outbreak phase. Reported case numbers were obtained from an open-access epidemiological database (https://github.com/globaldothealth/monkeypox). The shaded areas represent the 95% confidence interval related to parameters. (B) We quantified the impact of shortening the delay from disease onset to diagnostic confirmation. On average, a 9-day delay was reported at the early stage of the outbreak. The total number of infections by the end of 2022 was predicted for different states of the USA assuming the confirmation delay can be shortened to 5 or 3 days. (C) When simulating the effectiveness of ring vaccination, the median delay from symptom onset to confirmation was assumed to be 5 days. The efficacy of smallpox vaccines against monkeypox was estimated as 85% for both routine vaccination and ring vaccination.
