Figure 1.
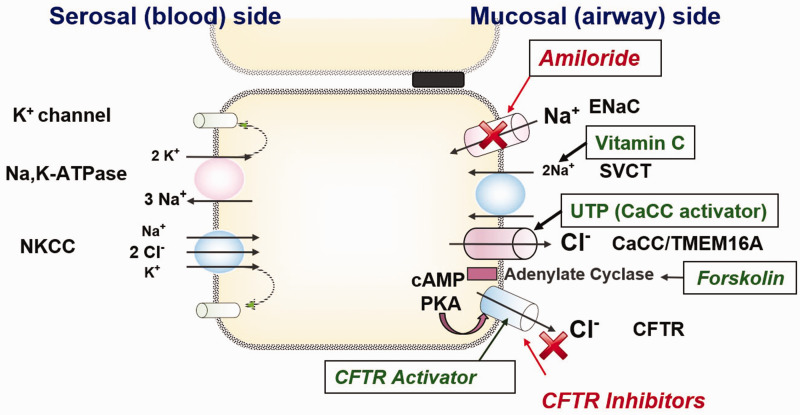
Ion transport and pharmacologic manipulation in airway epithelium. Transepithelial Na+ reabsorption mediated by concerted activity of apical epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC: Blocker = Amiloride) and the basolateral Na+/K+ ATPase. Apical located sodium dependent vitamin C transporter might also contribute to Na+ reabsorption. In addition to Na+ reabsorption airway, epithelia display a prominent apical Cl− secretion that is mainly mediated by the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in humans and to a lesser extent by Ca2+-dependent Cl− channels (CaCC) such as the TMEM channels. This secretion is kept up by the basolateral Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter (NKCC). In the basolateral membrane, several voltage-dependent K+ channels have been identified.