Table 1.
Synthetic methods of dicoumarols using different types of catalysts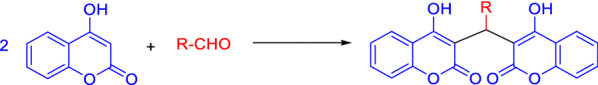
| Type of catalyst | Catalyst | Conditions | Dicoumarol derivatives R (yields) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lewis acids | I2 | I2 (10 mol%), H2O, 100 °C, 1 atm, 20–34 h |
Ph (97%), 2-HOC6H4 (98%) 3-O2NC6H4 (94%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-O2NC6H4 (95%), 4-HOC6H4 (98%) 4-MeOC6H4 (99%), –CH–CH–C6H4 (92%) Furan-2-yl (93%), thiophen-2-yl (91%) Indol-3-yl (95%), 3,4-piperonyl (96%) |
[45] |
| MnCl2 | MnCl2 (10 mol%), H2O, 100 °C, 20–40 min |
MeCH=CH– (95%), Ph (99%) 2-HOC6H4 (93%), 4-ClC6H4 (99%) 4-HOC6H4 (95%), 4-MeOC6H4 (97%) 4-O2NC6H4 (99%), furan-2-yl (96%) thiophen-2-yl (95%), indol-2-yl (94%) |
[46] | |
| Zn(Proline)2 | Zn(Proline)2 (5 mol%), H2O, reflux, 5–9 min |
Ph (92%), 2-ClC6H4 (96%) 2-HOC6H4 (92%), 3-O2NC6H4 (93%) 4-ClC6H4 (94%), 4-HOC6H4 (96%) 3-MeO-4-HOC6H3 (91%) thiophen-2-yl (93%) 5-Me-thiophen-2-yl (92%) pyridin-4-yl (91%) |
[47] | |
| InCl3 | InCl3 (10 mol%), H2O, MW, 110 °C, 15–20 min |
Ph (92%), 4-ClC6H4 (91%), 4-FC6H4 (93%) 4-HOC6H4 (90%), 4-MeC6H4 (85%) 4-MeOC6H4 (87%), 4-O2NC6H4 (96%) 4-HO-3-MeOC6H3 (89%) 3,4-(HO)2C6H3 (85%) 4-HO-3,5-(MeO)2C6H2 (86%) |
[48] | |
| Lewis and Bronsted acids | Sulfated titaniaa (TiO2/SO42−) | (TiO2/SO42−) (15%), H2O, 80 ºC, 12–30 min |
H (95%), Et (88%), Ph (92%), Pr (90%) iPr (90%), Me-CH=CH– (92%) 2-HOC6H4 (95%), 2-MeOC6H4 (85%) 2-O2NC6H4 (90%), 3-BrC6H4 (91%) 3-ClC6H4 (92%), 3-HOC6H4 (84%) 3-MeOC6H4 (88%), 3-O2NC6H4 (90%) 4-BrC6H4 (94%), 4-ClC6H4 (96%) 4-HOC6H4 (96%), 4-MeC6H4 (89%) 4-MeOC6H4 (92%), 4-O2NC6H4 (88%) 4-OH-3-MeOC6H3 (89%) 3-OH-4-MeOC6H3 (85%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (90%) 3,4,5-(MeO)3C6H2 (94%) 4-BnO-3-MeOC6H2 (82%) 4-CNC6H4 (96%), 4-Me2NC6H4 (89%) Ph-CH=CH– (86%), naphthalen-1-yl (85%) Furan-2-yl (90%) |
[49] |
| Inorganic acid salts | B(HSO4)3 | B(HSO4)3 (0.3 equiv) (1:1, H2O–EtOH), 70 °C, 3–6 min |
Ph (86%), 3-MeOC6H4 (81%) 3-O2NC6H4 (82%), 4-BrC6H4 (95%) 4-ClC6H4 (92%), 4-NCC6H4 (86%) 4-FC6H4 (88%), 4-MeC6H4 (87%) 4-MeOC6H4 (83%), 4-O2NC6H4 (98%) 4-Cl-3-O2NC6H3 (88%) |
[50] |
| Transition metals salts | RuCl3·nH2O | RuCl3·nH2O (5 mol%), H2O, 80 °C, 25–35 min |
Et (75%), Ph (84%), 4-ClC6H4 (85%) 4-NCC6H4 (95%), 4-MeOC6H4 (92%) 3-(PhO)-C6H4 (90%), 2-Cl-6-FC6H3 (92%) 3,4-(F2)C6H3 (90%) 2-HO-3-MeOC6H3 (84%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (84%), indol-3-yl (90%) 2-O2NC6H4CH=CH– (90%) |
[51] |
| Ionic liquids | [bmim]BF4 |
[bmim]BF4 (4 equiv) 60–70 °C, 2–3 h |
Ph (84%), 3-ClC6H4 (84%) 4-BrC6H4 (87%), 4-ClC6H4 (91%) 4-MeC6H4 (83%), 4-MeOC6H4 (87%) 4-O2NC6H4 (84%), Me2CH– (77%) Ph-CH=CH– (82%), furan-2-yl (83%) pyridin-2-yl (81%) |
[52] |
| SO3H-functionalized ILs based on benzimidazolium cation | [PSebim][OTf]b (10 mol%), 70 °C, 2–3 h |
Ph (95%), 3-BrC6H4 (94%) 3-ClC6H4 (94%), 4-BrC6H4 (95%) 4-ClC6H4 (96%), 4-MeC6H4 (93%) 4-MeOC6H4 (93%), 4-O2NC6H4 (96%) 4-(H2C=CH2)C6H4 (92%) |
[53] | |
| [MIM(CH2)4SO3H][HSO4] | [MIM(CH2)4SO3H] [HSO4] (15 mol%), 80 °C, 18–30 min |
Ph (92%), 2-ClC6H4 (88%) 2-O2NC6H4 (86%), 3-ClC6H4 (89%) 3-O2NC6H4 (89%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-MeC6H4 (90%), 4-MeOC6H4 (89%) 4-O2NC6H4 (96%) |
[54] | |
| Tetramethyl guanidium acetate ([TMG][Ac]) | [TMG][Ac] (0.75 mmol), rt, 0.5–4.5 h |
Ph (96%), 2-HOC6H4 (90%) 2-O2NC6H4 (92%), 3-O2NC6H4 (87%) 4-BrC6H4 (96%), 4-ClC6H4 (88%) 4-FC6H4 (93%), 4-F3CC6H4 (91%) 4-MeC6H4 (90%), 4-MeOC6H4 (86%) 4-O2NC6H4 (99%), pyridin-4-yl (87%)
(98%) |
[55] | |
| Choline hydroxide | ChOH (40%)c, 50 °C, 1–3 h |
H (quantitative), Ph (99%) 2-HOC6H4 (99%), 2-O2NC6H4 (75%) 3-O2NC6H4 (93%), 4-BrC6H4 (94%) 4-ClC6H4 (99%), 4-FC6H4 (99%) 4-F3CC6H4 (96%), 4-HOC6H4 (94%) 4-MeC6H4 (94%), 4-MeOC6H4 (95%) 4-HO-3-MeOC6H3 (93%), furan-2-yl (98%)
|
[56] | |
| [P4VPy-BuSO3H]Cl-X(AlCl3)d | IL (0.07 mmol), toluene, 90 °C, 0.5–0.9 h |
Ph (95%), 2-HOC6H4 (90%) 3-ClC6H4 (96%), 3-O2NC6H4 (96%) 4-ClC6H4 (93%), 4-MeC6H4 (94%) 4-MeOC6H4 (92%), 4-HOC6H4 (90%) 4-O2NC6H4 (96%), furan-2-yl (91%) Thiophen-2-yl (91%), pyridin-2-yl (91%) Ph–CH2–CH2 (92%), CH3CH2CH2– (92%) Ph-CH=CH– (93%) |
[57] | |
| [Dabco-H][AcO] | [Dabco-H][AcO] (10 mol%), H2O, 80 °C, 2–15 min |
n-Pr (99%), Ph (98%), 2-BrC6H4 (98%) 3-BrC6H4 (98%), 4-BrC6H4 (99%) 4-ClC6H4 (99%), 4-MeC6H4 (96%) 4-MeOC6H4 (98%), 4-O2NC6H4 (99%) 2,4-Cl2C6H3 (96%), naphthalen-2-yl (99%) thiophen-2-yl (98%), furan-2-yl (98%) |
[58] | |
| Hnmp/ZnCl3 | (Hnmp/ZnCl3) (20 mg), 100 °C, 30–50 min |
Ph (97%), 3-ClC6H4 (86%) 3-MeOC6H4 (90%), 3-O2NC6H4 (81%) 4-ClC6H4 (90%), 4-HOC6H4 (81%) 4-MeC6H4 (88%), 4-MeOC6H4 (93%) 4-O2NC6H4 (86%), 2,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (78%) pyridin-4-yl (90%) |
[59] | |
| Heteropoly acids (HPAs) | Phosphotungstic acid | HPA (15 mmol%), H2O, 80 °C, 14–25 min |
Ph (93%), 2-ClC6H4 (95%) 2-HOC6H4 (98%), 2-O2NC6H4 (96%) 3-O2NC6H4 (94%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-FC6H5 (98%), 4-HOC6H4 (98%) 4-MeOC6H4 (99%), 4-O2NC6H4 (95%) 2,4-Cl2C6H3 (92%), 2,6-Cl2C6H3 (98%) –CH=CH–C6H4 (98%), 3,4-piperonyl (96%) Indol-3-yl (95%), thiophen-2-yl (91%) Furan-2-yl (93%), 4-F3CC6H4 (98%) 4-Me2C6H3 (90%), 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (90%) |
[60] |
| Phase transfer catalysts and surfactants | Tetrabutyl ammonium bromide (TBAB)e,f | TBAB (10 mol%), H2O, 100 °C |
Ph (92%), 3-ClC6H4 (87%) 4-BrC6H4 (88%), 4-ClC6H4 (95%) 4-MeC6H4 (92%), 4-MeOC6H4 (84%) 4-O2NC6H4 (91%), Ph–CH=CH– (82%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (87%), Me2CH– (82%) 3,4,5-(MeO)3C6H2 (84%), piperonyl (88%) furan-2-yl (88%), pyridin-2-yl (90%) 4-(Me)2CHC6H4 (91%) |
[61] |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | SDS (20 mol%), H2O, 60 °C, 2.30–3.0 h |
Ph (90%), 2-MeC6H4 (84%) 3-ClC6H4 (92%), 3-O2NC6H4 (95%) 4-BrC6H4 (91%), 4-ClC6H4 (93%) 4-FC6H4 (94%), 4-MeC6H4 (97%) 4-(Me)2NC6H4 (94%), 4-MeOC6H4 (97%) 4-O2NC6H4 (98%), 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (98%) |
[62] | |
| Modified glycerols | Propane-1,2,3-triyl tris(hydrogen sulfate) (PTTH) | PTTH (0.03 mol%), 80 °C, H2O, 7–10 ming or solvent-free, 5–8 min |
H (80%), Ph (90%), 2-ClC6H4 (85%) 3-O2NC6H4 (95%), 4-ClC6H4 (90%) 4-HOC6H4 (85%), 4-MeC6H4 (90%) 4-MeOC6H4 (85%), 4-O2NC6H4 (95%) 3,4-(MeO)2C6H3 (85%), Ph-CH=CH– (85%) furan-2-yl (80%) |
[63] |
aThe catalyst possesses as many Lewis acid sites as Bronsted acid sites. The superacidity is due to the Bronsted acidic hydroxy groups attached to Ti atom, being generated by interaction with water. The acidity is enhanced by the generation of Lewis acid sites due to—I effect exerted by attached SO42− ions to Ti atoms. These factors promote the overall reaction by activating the aldehydes and the Michael acceptor
b[PSebim][OTf]=1-ethyl-3-(3-sulfopropyl)-benzimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate
cAmount of catalyst is 1.5 equiv. relative to the aldehyde
d[P4VPy-BuSO3H]Cl-X(AlCl3) is poly(4-vinylpyridine-co-1-sulfonic acid butyl-4-vinylpyridinium)chloroaluminate, a supported ionic liquid with both Lewis and Brønsted acid sites
eThis catalyst was also used in the synthesis of dicoumarol derivatives under solvent-free conditions. The reaction times were slightly shortened in neat conditions, and the yields were also slightly lower
fTBAF was found to be equally effective as catalyst
gYields for the reaction in water indicated in the table

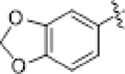 3-MeO-4-HOC6H3 (84%), furan-2-yl (95%)
3-MeO-4-HOC6H3 (84%), furan-2-yl (95%)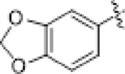 4-O2NC6H4 (89%), pyridin-4-yl (81%) (95%)
4-O2NC6H4 (89%), pyridin-4-yl (81%) (95%)