Figure 3.
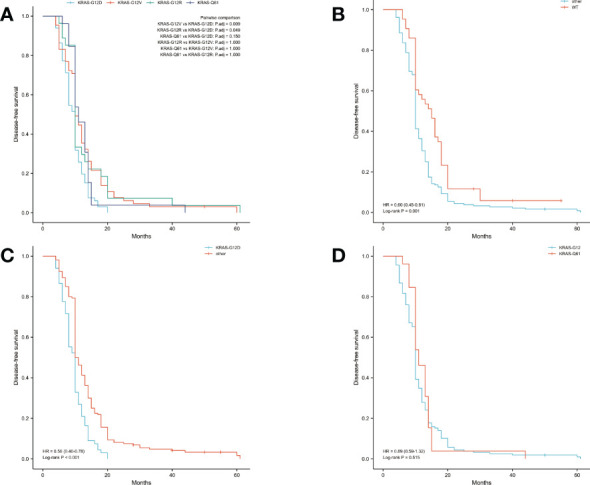
Disease-free survival (DFS) in all patients was examined with Kaplan-Meier plots and log-rank tests. (A) Comparison of four groups (KRAS-G12D, KRAS-G12V, KRAS-G12R, KRAS-Q61) with KRAS mutations. (B) Evaluation of KRAS mutation carriers against individuals with the wild-type gene. Additional subsets were denoted by the names KRAS-G12D, KRAS-G12V, KRAS-G12R, and KRAS-Q61. (C) Those with the KRAS-G12D mutation were compared to those without it and vice versa. Wild-type KRAS, KRAS-G12V, KRAS-G12R, and KRAS-Q61 were the other subsets. (D) A comparison of the mutations at codons 12 and 61. The KRAS-G12D, V, and R codon 12 groups were present. The KRAS-Q61H, Q61R, Q61K, and Q61L codons were part of the codon 61 group. WT, KRAS wild-type; HR, hazard ratio; The numbers in parentheses represent 95% confidence intervals.
